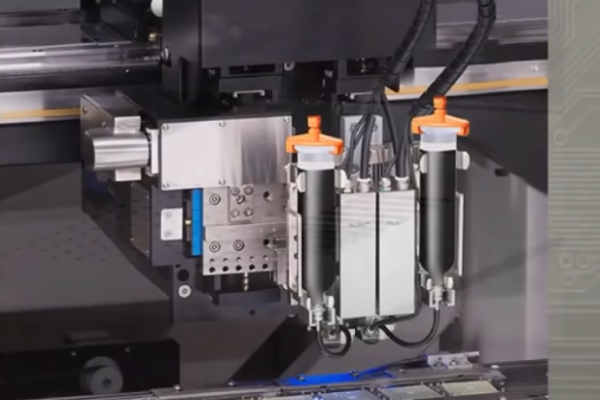
Overview of Jetting Valves and Their Significance in Manufacturing Processes
Jetting valves are advanced dispensing technologies that enable high-speed, non-contact application of various fluids in manufacturing processes. They are particularly valuable for industries requiring precise fluid dispensing, such as electronics, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
Key Features of Jetting Valves
- Non-Contact Dispensing: Jetting valves operate without the need for Z-axis movement, allowing fluids to be ejected from the valve directly onto the substrate. This method minimizes the risk of damage to fragile components and eliminates wear on dispensing tips.
- High Speed and Precision: These valves can achieve dispensing speeds up to 1000 Hz continuously and even higher in bursts (up to 1500 Hz). This capability significantly enhances production efficiency compared to traditional contact dispensing methods, which can be substantially slower.
- Versatility in Fluid Types: Jetting valves can dispense a wide range of materials, including adhesives, oils, greases, and even challenging substances like cyanoacrylate adhesives and solder pastes. They can handle viscosities up to 2,000,000 mPa.s, making them suitable for various applications.
- Small Deposit Sizes: Jetting technology allows for the precise application of very small fluid volumes, often less than 1 nanoliter (nL). This is particularly important as components become smaller and more intricate in modern manufacturing.
- Adaptability to Surface Irregularities: Jetting valves can effectively dispense materials onto uneven surfaces or complex geometries without compromising accuracy or efficiency. This feature is crucial for applications where traditional contact methods would struggle.
Significance in Manufacturing Processes
- Increased Productivity: By eliminating the need for Z-axis movement and enabling rapid dispensing, jetting valves contribute to higher throughput in production lines. This efficiency is vital as manufacturers aim to reduce costs while maintaining quality.
- Improved Quality Control: The precision of jetting valves allows for consistent application of materials within tight tolerances, reducing the likelihood of defects and rework. This reliability is essential in high-stakes industries like electronics assembly.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although initial investments in jetting valve technology may be higher than traditional methods, the long-term savings from reduced downtime, lower material waste, and enhanced productivity often justify the expense. Additionally, advancements in valve design have improved maintenance processes, further reducing operational costs.
- Innovation Facilitation: As manufacturing processes evolve towards miniaturization and complexity, jetting valves support innovation by allowing manufacturers to explore new designs and applications that were previously challenging or impossible with older dispensing technologies.
Jetting valves represent a significant advancement in fluid dispensing technology within manufacturing processes. Their ability to dispense materials quickly and accurately without contact makes them indispensable for modern production environments focused on efficiency, quality, and adaptability. As industries continue to innovate and demand more precise manufacturing solutions, jetting valves will play a crucial role in meeting these challenges.
Importance of selecting the right jetting valve for specific applications
Selecting the right jetting valve is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as it directly impacts efficiency, accuracy, and the quality of the final product. Here are several key considerations that highlight the importance of this decision:
1. Application Specificity
Different applications require different dispensing characteristics. Jetting valves can be tailored to handle a variety of fluids, including adhesives, oils, and solder pastes. For instance, piezoelectric jetting valves are ideal for precise micro-deposits (as small as 0.5 nL), which is essential in applications like electronics assembly where component sizes are shrinking. Conversely, pneumatic valves may be better suited for thicker materials or those requiring larger deposit sizes.
2. Speed and Efficiency
Jetting valves offer high-speed dispensing capabilities, with some models capable of operating at frequencies up to 3000 Hz. This speed allows for rapid production cycles and minimizes downtime compared to traditional contact dispensing methods that require Z-axis movement. The ability to dispense at such high rates is particularly beneficial in high-volume manufacturing environments where time savings translate directly into cost efficiency.
3. Precision and Consistency
The accuracy of fluid deposition is critical in many manufacturing processes. Jetting valves provide non-contact dispensing, which reduces the risk of damage to delicate components and enhances repeatability. For applications requiring stringent quality control, such as in medical device manufacturing, selecting a valve with high precision capabilities—like the piezoelectric models—ensures that each deposit meets exact specifications.
4. Fluid Compatibility
Choosing a valve that is compatible with the specific fluid type being dispensed is essential. For example, pneumatic valves are often recommended for higher viscosity fluids due to their ability to generate sufficient pressure to push thick materials through the nozzle. Understanding the rheological properties of the fluid can guide manufacturers in selecting the most appropriate jetting technology.
5. Surface Adaptability
Jetting valves excel in dispensing onto irregular surfaces or complex geometries without compromising accuracy. This adaptability is vital for modern manufacturing processes where components may not have uniform surfaces. Selecting a valve that can handle these variations ensures consistent application across diverse substrates.
6. Cost Considerations
While advanced jetting systems may have higher upfront costs, their efficiency and reduced waste can lead to lower overall production costs in the long run. Factors such as maintenance requirements, consumable replacement rates, and operational longevity should be evaluated when considering the total cost of ownership.
The selection of a jetting valve should be guided by a thorough understanding of the specific application requirements, including fluid characteristics, desired speed and precision, surface conditions, and cost implications. Engaging with experienced application specialists can further aid in identifying the most suitable technology for achieving optimal manufacturing outcomes.
How Jetting Valves Work

Jetting Valves: Mechanism of Operation
Jetting valves are sophisticated devices used for non-contact fluid dispensing in various manufacturing applications. They operate by ejecting small amounts of fluid in precise patterns, making them ideal for tasks that require accuracy and speed.
Jetting Process Explained
- Fluid Preparation: The fluid to be dispensed is stored in a reservoir connected to the jetting valve. Depending on the application, this fluid can range from low-viscosity adhesives to high-viscosity pastes.
- Actuation: The valve is actuated by either pneumatic or electric means. When activated, a mechanism within the valve creates a pressure pulse that forces the fluid through a nozzle.
- Jet Formation: The fluid exits the nozzle in a controlled jet stream, forming droplets or beads depending on the desired application. This process can occur at high frequencies, allowing for rapid dispensing cycles.
- Dispensing Control: Advanced control systems regulate the timing and volume of each dispense cycle, ensuring that the correct amount of fluid is applied consistently.
Types of Actuation
Jetting valves can be actuated using different technologies, each suited for specific applications:
- Pneumatic Actuation: This method uses compressed air to create pressure that opens and closes the valve. Pneumatic jetting valves are known for their speed and ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities. They are particularly effective for medium to high-viscosity fluids and can achieve rapid dispensing rates (up to 150 Hz) with precise control over deposit sizes ranging from 3 nL to 200 nL .
- Electric Actuation: Electric jetting valves utilize piezoelectric technology to achieve precise control over dispensing. This type of actuation allows for extremely fine deposits (as small as 0.5 nL) and high-frequency operation (up to 3000 Hz) . Electric actuators are often preferred for applications requiring high precision and repeatability, such as in electronics or medical device manufacturing.
Overview of Control Systems
Control systems play a critical role in the operation of jetting valves, ensuring accurate and efficient dispensing:
- Dedicated Controllers: Many jetting valves come with specialized controllers that manage the actuation process. For example, controllers like the PICO Toµch XP provide user-friendly interfaces for setting parameters such as stroke length and frequency . These controllers facilitate quick adjustments and calibration, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC): Some systems allow integration with PLCs for more complex manufacturing environments. This flexibility enables manufacturers to incorporate jetting valves into automated production lines seamlessly .
- Feedback Mechanisms: Advanced control systems may include sensors that provide real-time feedback on dispensing performance. This data allows for continuous adjustments during operation, ensuring consistent quality and reducing waste.
The mechanism of operation for jetting valves involves a sophisticated interplay between fluid dynamics, actuation technology, and control systems. Selecting the appropriate type of actuation—whether pneumatic or electric—and implementing an effective control system is essential for maximizing efficiency and precision in various manufacturing applications. Understanding these components allows manufacturers to optimize their processes and achieve superior results in fluid dispensing tasks.
Jetting Valves: Common Features
Jetting valves are essential components in modern fluid dispensing systems, particularly in high-speed manufacturing processes. Understanding their common features, including key components and adjustability, is crucial for selecting the right valve for specific applications 1.
Key Components
- Nozzles:
- Function: The nozzle is critical for controlling the size and shape of the fluid deposit. Different nozzle sizes can be used to achieve various droplet volumes, ranging from as small as 0.5 nL to larger deposits depending on the application.
- Types: Jetting valves often come with interchangeable nozzles, allowing customization based on the fluid’s viscosity and the desired deposit size. For instance, some valves can accommodate nozzle diameters from 20 µm up to 1.4 mm.
- Fluid Reservoirs:
- Function: These reservoirs hold the fluid before it is dispensed. They are designed to maintain consistent pressure and flow to ensure reliable dispensing.
- Integration: Many jetting systems include dedicated controllers that manage fluid delivery from the reservoir to the valve, ensuring optimal performance.
- Actuation Mechanism:
- Jetting valves can be pneumatically or electrically actuated. Pneumatic valves use compressed air to operate, while piezoelectric valves utilize electrical energy to achieve rapid movement and precise control of fluid ejection.
- Tappets:
- Role: Tappets are components that help in ejecting the fluid from the nozzle by creating pressure within the valve chamber. Their design can affect the valve’s responsiveness and accuracy in dispensing.
- Customization: Many jetting valves feature easily exchangeable tappets to adapt to different fluid types and dispensing requirements.
Adjustability and Settings for Different Applications
- Volume Control:
- Jetting valves allow for precise control over the volume of fluid dispensed per cycle. This is crucial for applications requiring specific amounts of adhesive or other materials, enabling manufacturers to minimize waste and ensure consistency.
- Frequency Settings:
- The dispensing frequency can be adjusted based on production needs. Some jetting valves can operate at speeds up to 3000 Hz, making them suitable for high-volume applications where rapid dispensing is essential.
- Pressure Adjustments:
- The pressure at which fluids are dispensed can also be modified, particularly in pneumatic systems where air pressure influences fluid flow and consistency. This adjustability helps accommodate a wide range of viscosities, from low to high.
- Temperature Control:
- Some jetting systems include heating elements that allow for temperature adjustments, which can improve fluid flow characteristics, especially for thicker materials.
- User Interfaces:
- Modern jetting systems often come with user-friendly interfaces that facilitate easy adjustments of settings such as stroke length, timing, and operational modes (e.g., timed mode or continuous mode). This flexibility enables quick adaptations to changing production requirements.
The common features of jetting valves—such as their key components (nozzles, fluid reservoirs, actuation mechanisms) and their adjustability—play a significant role in their effectiveness across various applications. By understanding these features, manufacturers can select and configure jetting valves that best meet their specific dispensing needs, ultimately enhancing productivity and product quality in their operations.
Jetting Valves Applications Across Industries
Electronics Manufacturing
Jetting valves play a critical role in electronics manufacturing, particularly in PCB assembly and component placement. Their unique dispensing capabilities enhance efficiency, precision, and flexibility in various applications.
Role in PCB Assembly
- Non-Contact Dispensing: Jetting valves operate without requiring Z-axis movement, allowing fluid to be dispensed from above the PCB. This non-contact method is ideal for delicate components, as it reduces the risk of damage during the dispensing process. The ability to dispense materials without direct contact also allows for greater tolerance in part positioning and tooling setups.
- High-Speed Operation: Jetting valves can achieve dispensing speeds of up to 3000 Hz, significantly faster than traditional contact valves. This speed is crucial in high-volume production environments where rapid application of adhesives, solder pastes, or other materials is necessary to maintain throughput and efficiency.
- Precision and Miniaturization: As electronic components continue to miniaturize, the demand for smaller and more precise deposits increases. Jetting valves can dispense micro-deposits as small as 0.5 nL, accommodating the need for tiny beads and lines essential in modern PCB assembly processes.
- Versatility in Material Handling: Jetting valves are capable of dispensing a wide range of materials, including low to high viscosity fluids like adhesives, greases, and solder pastes. This versatility makes them suitable for various applications within PCB assembly, such as underfill processes, edge sealing, and bonding components.
- Adaptability to Complex Geometries: The ability of jetting valves to dispense accurately onto irregular surfaces or complex geometries is particularly beneficial in PCB assembly. They can effectively apply materials into grooves, cavities, or onto vertical faces without compromising quality or consistency
Component Placement
- Accurate Component Placement: Jetting valves facilitate precise placement of adhesives used for securing components onto PCBs. Their high accuracy ensures that adhesives are applied exactly where needed, minimizing waste and enhancing the reliability of the assembly process.
- Integration with Automation: Many jetting valve systems can be integrated into automated production lines, allowing for synchronized operation with pick-and-place machines. This integration streamlines the entire assembly process and enhances overall productivity by reducing manual handling and errors.
- Control Systems: Advanced control systems associated with jetting valves enable manufacturers to fine-tune dispensing parameters such as volume, pressure, and timing. This level of control is essential for achieving consistent results across different batches of PCBs.
Jetting valves are integral to electronics manufacturing, particularly in PCB assembly and component placement. Their non-contact dispensing capabilities, high-speed operation, precision handling of micro-deposits, versatility with various materials, and adaptability to complex geometries make them indispensable tools in achieving efficient and reliable manufacturing processes. As technology continues to advance in the electronics sector, the role of jetting valves will likely expand further, supporting the ongoing trends towards miniaturization and complexity in electronic devices.
Automotive Industry
Jetting valves are increasingly important in the automotive industry, particularly for the dispensing of adhesives and sealants during various manufacturing processes. Their unique capabilities enhance efficiency, precision, and flexibility in applications critical to automotive assembly.
Role of Jetting Valves in Adhesive and Sealant Dispensing
- Non-Contact Dispensing:
- Jetting valves operate using a non-contact method, allowing fluids to be dispensed without direct contact with the substrate. This feature is particularly beneficial in automotive manufacturing, where components can be delicate or have intricate geometries. The non-contact nature minimizes the risk of damage and contamination, ensuring that adhesives and sealants are applied precisely where needed without affecting adjacent components.
- High-Speed Operation:
- Jetting valves can dispense materials at impressive speeds, often reaching up to 3000 Hz. This high throughput is essential in automotive production lines where efficiency is paramount. The ability to quickly apply adhesives and sealants allows manufacturers to maintain fast production cycles while ensuring consistent application quality.
- Precision and Miniaturization:
- As automotive components become smaller and more complex, the need for precise adhesive application increases. Jetting valves can dispense micro-deposits as small as 0.5 nL, accommodating the growing trend towards miniaturization in automotive design. This precision is crucial for applications such as bonding sensors, sealing electronic components, and applying underfill materials.
- Versatility with Various Materials:
- Jetting valves are capable of dispensing a wide range of materials, including low to high viscosity adhesives, sealants, greases, and even more challenging substances like cyanoacrylate adhesives. This versatility makes them suitable for various applications within the automotive sector, such as edge sealing, potting, bonding structural components, and applying conformal coatings.
- Adaptability to Complex Geometries:
- The ability of jetting valves to accurately dispense materials onto irregular surfaces or into tight spaces is particularly advantageous in automotive manufacturing. They can effectively apply adhesives into grooves, cavities, or onto vertical surfaces without compromising accuracy or quality. This adaptability ensures that even complex assemblies receive the necessary adhesive coverage.
- Integration with Automation:
- Jetting valves can be easily integrated into automated production lines and robotic systems. This integration enhances overall process efficiency by synchronizing adhesive dispensing with other manufacturing operations such as component placement and assembly. Dedicated controllers facilitate precise control over dispensing parameters such as volume and timing, further optimizing production workflows.
Jetting valves play a vital role in the automotive industry by enhancing the dispensing of adhesives and sealants through their non-contact operation, high-speed capabilities, precision handling of micro-deposits, versatility with various materials, adaptability to complex geometries, and seamless integration with automated systems. As automotive manufacturing continues to evolve towards greater efficiency and complexity, the importance of jetting valves in achieving these goals will only increase.
Jetting Valves Medical Devices
Jetting valves are increasingly utilized in the medical device industry for precision applications in device assembly. Their unique features enable accurate and efficient dispensing of various materials, which is critical in ensuring the reliability and performance of medical devices.
Precision Applications in Device Assembly
- Non-Contact Dispensing:
- Jetting valves operate using a non-contact method, allowing materials to be dispensed without direct contact with the substrate. This is particularly important in medical device manufacturing, where components may be sensitive or require strict contamination control. The non-contact nature minimizes the risk of damage and ensures that adhesives or sealants are applied accurately without affecting adjacent components.
- High-Speed and High-Frequency Operation:
- These valves can dispense materials at high speeds, often exceeding 1000 Hz, which allows for rapid application of adhesives and sealants during assembly processes. This capability is essential for maintaining high throughput in production lines while ensuring consistent quality.
- Micro-Dispensing Capabilities:
- Jetting valves can deliver extremely small volumes of material, with deposits as low as 0.5 nL. This precision is crucial for applications such as bonding miniature components, applying underfills in micro-electronic packages, and sealing delicate assemblies where excess material could compromise functionality.
- Versatility with Various Materials:
- Jetting valves can handle a wide range of fluids, including low to high viscosity adhesives, sealants, and even challenging materials like cyanoacrylate adhesives. This versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications within the medical device sector, from assembling sensors to potting electronic components.
- Adaptability to Complex Geometries:
- The ability to dispense materials onto irregular surfaces or complex geometries is a significant advantage of jetting valves. They can effectively apply adhesives into grooves, cavities, and onto vertical surfaces without compromising accuracy or quality, which is often required in intricate medical device designs.
- Integration with Automation:
- Jetting valves can be seamlessly integrated into automated production systems, enhancing overall process efficiency. This integration allows for synchronized operation with robotic arms or conveyor systems, ensuring that adhesive dispensing occurs simultaneously with other assembly operations.
- Control Systems for Precision:
- Advanced control systems associated with jetting valves enable precise adjustments of dispensing parameters such as volume, pressure, and timing. This level of control is essential for achieving consistent results across different batches of medical devices and ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Jetting valves play a vital role in the assembly of medical devices by providing precise, efficient, and versatile dispensing capabilities. Their non-contact operation, high-speed performance, micro-dispensing abilities, and adaptability to complex geometries make them indispensable tools in modern medical manufacturing processes. As the demand for smaller and more intricate medical devices continues to grow, the importance of jetting valves in achieving these goals will only increase.
Packaging
Jetting valves are increasingly utilized in packaging applications, particularly for labeling and sealing processes. Their ability to dispense materials accurately and efficiently makes them ideal for various tasks within the packaging industry.
Applications in Labeling
- Non-Contact Dispensing:
- Jetting valves allow for non-contact application of adhesives used in labeling, which minimizes the risk of damaging delicate labels or substrates. This feature is particularly beneficial when working with sensitive materials or intricate designs.
- High-Speed Operation:
- These valves can operate at high speeds (up to 3000 Hz), enabling rapid application of adhesive dots or lines needed for labels. This speed is essential in high-volume production environments where efficiency and throughput are critical.
- Precision and Consistency:
- Jetting valves can dispense micro-deposits as small as 0.5 nL, ensuring precise application of adhesives for labels. This precision helps reduce material waste and ensures that each label is securely affixed without excess adhesive that could lead to messiness or product defects.
- Versatility with Various Adhesives:
- Jetting valves can handle a wide range of adhesives, including low to high viscosity options, making them suitable for different types of labels and packaging materials. This versatility allows manufacturers to adapt their labeling processes based on specific product requirements.
- Adaptability to Complex Shapes:
- The ability to dispense accurately onto irregular surfaces or complex geometries makes jetting valves ideal for labeling products with unique shapes or contours. They can effectively apply adhesive in tight spaces or around curves without compromising accuracy.
Applications in Sealing
- Sealing Applications:
- Jetting valves are also used for applying sealants in packaging processes. Their non-contact dispensing capability allows for the precise application of sealants around edges, seams, or closures without direct contact with the substrate.
- High Throughput and Efficiency:
- The high-speed dispensing capabilities of jetting valves contribute to faster sealing processes, which is crucial in high-volume packaging operations where time efficiency is paramount.
- Elimination of Dripping and Stringing:
- One significant advantage of jetting technology is its ability to eliminate dripping and stringing, common issues with traditional dispensing methods. This characteristic ensures clean and professional-looking seals, enhancing the overall quality of the packaged product.
- Integration with Automated Systems:
- Jetting valves can be easily integrated into automated packaging lines, allowing synchronized operation with other processes such as filling, labeling, and boxing. This integration streamlines production workflows and improves overall efficiency.
- Control Over Deposit Size:
- The precise control offered by jetting valves allows manufacturers to adjust the amount of sealant dispensed according to specific requirements, ensuring optimal performance while minimizing waste.
Jetting valves play a vital role in packaging applications, particularly in labeling and sealing processes. Their non-contact dispensing capabilities, high-speed operation, precision handling of micro-deposits, versatility with various adhesives and sealants, and adaptability to complex shapes make them indispensable tools in modern packaging operations. As manufacturers continue to seek improvements in efficiency and product quality, the importance of jetting valves in achieving these goals will only grow.
Brand Comparisons: Axxon Mycronic, Anda Technologies, Vermes, Nordson Efd, Nordson Asymtek

Axxon Mycronic Jetting Valves
Axxon Mycronic jetting valves are advanced dispensing solutions designed for high precision and efficiency in various applications, particularly in electronics and medical device manufacturing. Below is an overview of their specifications, features, performance, and applications.
Specifications
- Fluid Compatibility:
- Designed to handle a wide range of viscosities, from low (1 cps) to high (200,000 cps).
- Suitable for dispensing adhesives, sealants, and other fluids commonly used in manufacturing.
- Dispensing Volume:
- Capable of dispensing micro-deposits as small as 0.5 nL.
- Typical deposit volumes range from 3 nL to 200 nL depending on the specific valve model.
- Actuation Technology:
- Available in both pneumatic and piezoelectric configurations.
- Pneumatic models typically operate at pressures between 4 to 10 bar.
- Speed and Frequency:
- High-speed operation with dispensing frequencies up to 3000 Hz for continuous applications.
- Burst mode capabilities can reach even higher frequencies for specific tasks.
- Control Systems:
- Operated through dedicated controllers that allow precise control over dispensing parameters such as volume, timing, and pressure.
- Integration with PLCs for automated systems is supported.
- Materials of Construction:
- Wetted parts made from durable materials such as stainless steel, tungsten carbide, and PEEK to withstand various fluids and operational conditions.
- Nozzle seals typically utilize Teflon for enhanced durability.
Features
- Modular Design:
- Many models feature modular components that allow for easy maintenance and part replacement without extensive downtime.
- Customizable Nozzles:
- Easily interchangeable nozzles enable customization based on the specific application requirements regarding fluid type and deposit size.
- User-Friendly Interfaces:
- Controllers often include touchscreen interfaces for straightforward setup and adjustments, making it easier for operators to manage dispensing processes.
- Non-Contact Dispensing:
- Jetting valves utilize non-contact technology to minimize the risk of damage to sensitive components during the dispensing process.
Performance
- Precision:
- Jetting valves deliver high precision in material application, which is critical in industries where accuracy is paramount, such as electronics assembly and medical device manufacturing.
- Consistency:
- The ability to maintain consistent deposit sizes contributes to high-quality production standards and reduces material waste.
- Reduced Downtime:
- Quick part replacement and easy maintenance help minimize production interruptions.
Applications
- Electronics Manufacturing:
- Used for solder paste application, adhesive bonding, and underfill processes in PCB assembly. Their precision is essential for assembling miniature components and ensuring reliable connections.
- Medical Device Assembly:
- Ideal for applications requiring strict adherence to cleanliness standards, such as applying adhesives in device assembly or sealing sensitive electronic components within medical devices.
- Automotive Industry:
- Employed for dispensing lubricants, adhesives, and sealants in automotive parts assembly, ensuring efficient production while maintaining quality standards.
- Packaging Applications:
- Utilized in labeling and sealing processes where precise adhesive application is necessary to ensure product integrity.
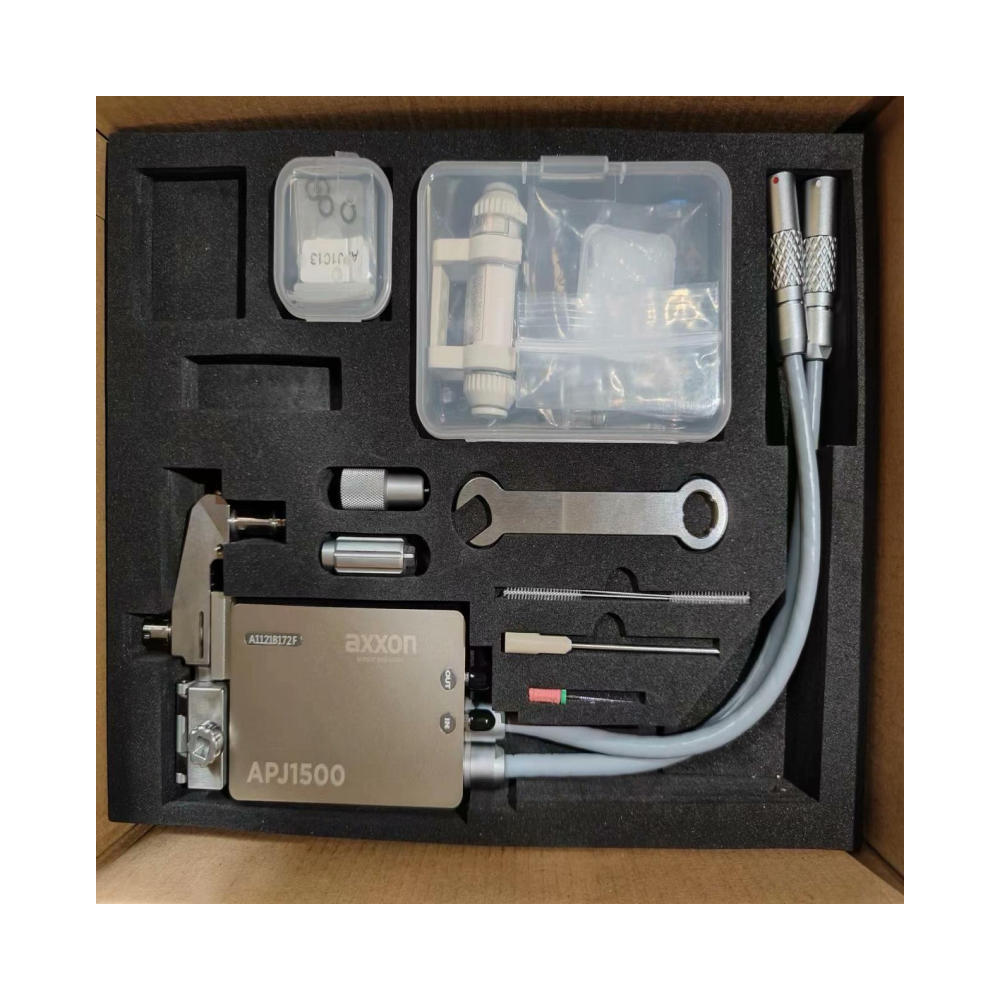
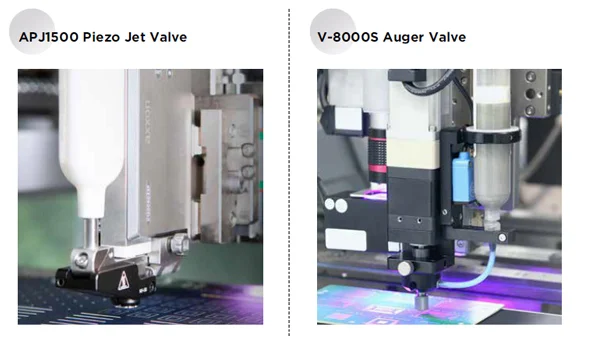
Valves we can supply: APJ1500 Piezo Jetting Valve, APJ2000 Piezo Jetting Valve, APJ3000 Piezo Jetting Valve, V-8000S Aguer Valve, APJ1000 Piezo Jetting Valve .
Axxon Mycronic jetting valves are versatile tools that enhance manufacturing efficiency across various industries by providing precise, reliable, and customizable dispensing solutions. Their advanced features cater to the demands of modern production environments where accuracy and speed are critical.
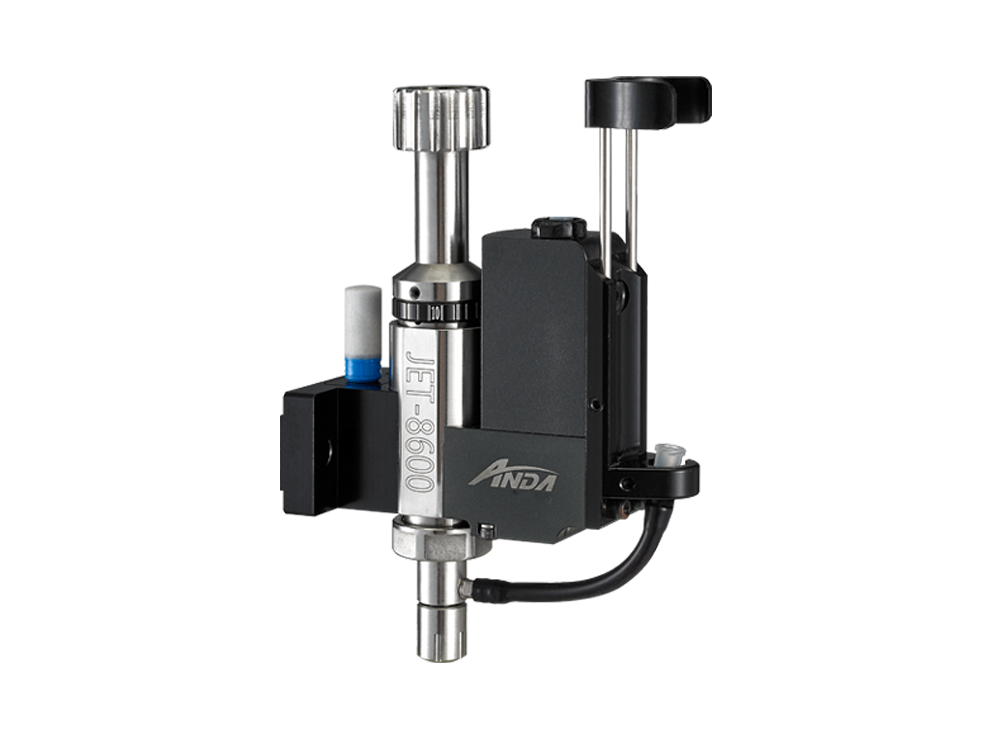
Anda Technologies Jetting Valves
Anda Technologies offers a range of jetting valves designed for high precision and efficiency in dispensing applications across various industries. Below is an overview of their specifications, features, performance, and applications.

Specifications
- Fluid Compatibility:
- Capable of dispensing low to high viscosity fluids, including adhesives, sealants, and greases.
- Dispensing Volume:
- Typical dot sizes achievable range from 0.3 mm upwards, with micro shot sizes as small as 0.5 nL depending on the fluid type.
- Actuation Technology:
- Available in both pneumatic and piezoelectric configurations, allowing for flexibility based on application needs.
- Speed and Frequency:
- High-speed operation with dispensing frequencies that can exceed 200 Hz, enabling rapid application cycles.
- Control Systems:
- Operated through dedicated controllers that allow precise adjustments of dispensing parameters such as volume and timing.
- Materials of Construction:
- Wetted parts are typically made from durable materials like stainless steel and tungsten carbide to withstand various fluids and operational conditions.
Features
- Non-Contact Dispensing:
- Jetting valves utilize a non-contact method to apply fluids, which reduces the risk of damaging sensitive components during the dispensing process.
- Modular Design:
- Many models feature a modular design that allows for easy maintenance and part replacement, minimizing downtime during production.
- User-Friendly Interfaces:
- Controllers often include touchscreen interfaces for straightforward setup and adjustments, making it easier for operators to manage dispensing processes.
- Fine-Tuning Settings:
- The ability to adjust parameters such as material pressure and jetting pressure enhances the accuracy and consistency of fluid deposition.
Performance
- Precision and Consistency:
- Anda jetting valves deliver high precision in material application, ensuring consistent results across different batches. The ability to maintain small deposit sizes contributes to reduced material waste.
- High Throughput:
- With fast dispensing capabilities, these valves support high-volume production environments where efficiency is critical.
- Reduced Downtime:
- Quick part replacement and easy maintenance help minimize production interruptions, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
Applications
- Electronics Manufacturing:
- Used for solder paste application, adhesive bonding, and underfill processes in PCB assembly. Their precision is essential for assembling miniature components and ensuring reliable connections.
- Medical Device Assembly:
- Ideal for applications requiring strict adherence to cleanliness standards, such as applying adhesives in device assembly or sealing sensitive electronic components within medical devices.
- Automotive Industry:
- Employed for dispensing lubricants, adhesives, and sealants in automotive parts assembly, ensuring efficient production while maintaining quality standards.
- Packaging Applications:
- Utilized in labeling and sealing processes where precise adhesive application is necessary to ensure product integrity.
Valves we can supply: JET-8600 Peumatic Jetting Valve, TDS-25 Contacting Slide Valve, PC2000 Two-component Screw Valve, PC1000 Single Component Screw Valve, PV-20 Quick Release Piezo Valve, PV-20HM Hot Melt Valve, SV-06 Quick Release Screw Valve, DJ-01 Needle Valve, HV-01 High Pressure Valve, ZS-02 Needle Atomization Valve, LA-W30 Sector Spray Valve, SA-W6L Small Atomization Valve, IC-100L Thin Film Valve, NV-04 MINI Precise Atomization Valve,
Anda Technologies jetting valves are versatile tools that enhance manufacturing efficiency across various industries by providing precise, reliable, and customizable dispensing solutions. Their advanced features cater to the demands of modern production environments where accuracy and speed are critical. As manufacturers continue to seek improvements in efficiency and product quality, the importance of Anda jetting valves in achieving these goals will only grow.
VERMES Jetting Valves
VERMES jetting valves are advanced dispensing solutions designed for high precision and efficiency across various industrial applications. Below is an overview of their specifications, features, performance, and applications.

Specifications
- Fluid Compatibility:
- Capable of dispensing a wide range of materials, including adhesives, solder pastes, inks, oils, greases, and aqueous solutions.
- Viscosity range: Up to 2,000,000 mPas.
- Dispensing Volume:
- Minimum shot size of less than 1 nL, with the ability to dispense larger volumes as needed (up to >20 μL).
- Actuation Technology:
- Utilizes Dynamic Shockwave Technology (DST) for precise actuation.
- Available in configurations that allow for both pneumatic and electric actuation.
- Speed and Frequency:
- Maximum dispensing frequency of up to 700 Hz (average around 500 Hz), enabling rapid application cycles.
- Control Unit Dimensions:
- Control unit dimensions: 128 mm x 51 mm x 189 mm.
- Control unit weight: Approximately 550 g.
- Valve Dimensions:
- Valve dimensions: 100 mm x 35 mm x 90 mm.
- Valve weight: Approximately 390 g.
- Inlet Pressure Range:
- Inlet pressure range: 0.1 to 100 bar (specific ranges depending on the configuration).
Features
- Dynamic Shockwave Technology (DST):
- This innovative actuator principle optimizes yield and enhances precision during dispensing operations.
- Integrated Heating System:
- The valve includes a heating system that maintains consistent material temperatures for optimal viscosity during dispensing.
- Modular Design:
- The fluid box is easily removable for quick cleaning or material changes without additional tools.
- Easy Setup and Adjustment:
- Parameters can be modified on-the-fly, allowing for quick adjustments to dispensing patterns and volumes.
- Versatile Mounting Options:
- The valve can be mounted from any of three sides, providing flexibility in integration with automation or robotics.
Performance
- Precision and Repeatability:
- The VERMES jetting valves are known for their high accuracy and repeatability in dispensing small volumes, making them suitable for applications requiring stringent quality control.
- High Throughput:
- With fast dispensing capabilities, these valves support high-volume production environments while maintaining consistent quality.
- Reduced Downtime:
- The design facilitates quick maintenance and part replacement, minimizing production interruptions.
Applications
- Electronics Manufacturing:
- Ideal for solder paste application, adhesive bonding, and underfill processes in PCB assembly. Their precision is essential for assembling miniature components reliably.
- Medical Device Assembly:
- Suitable for applications requiring strict cleanliness standards, such as applying adhesives in device assembly or sealing sensitive electronic components within medical devices.
- Automotive Industry:
- Used for dispensing lubricants, adhesives, and sealants in automotive parts assembly to ensure efficient production while maintaining quality standards.
- Consumer Goods:
- Employed in the packaging of consumer products where precise adhesive application is necessary for labels and seals.
- General Manufacturing:
- Versatile enough to be used in various manufacturing processes across different industries where accurate fluid dispensing is critical.
VERMES jetting valves provide a robust solution for precision dispensing across multiple industries. Their advanced technology, high-speed capabilities, and versatility make them invaluable tools in modern manufacturing processes where accuracy and efficiency are paramount. As industries continue to evolve towards more complex products and processes, the role of VERMES jetting valves will remain significant in achieving optimal production outcomes.
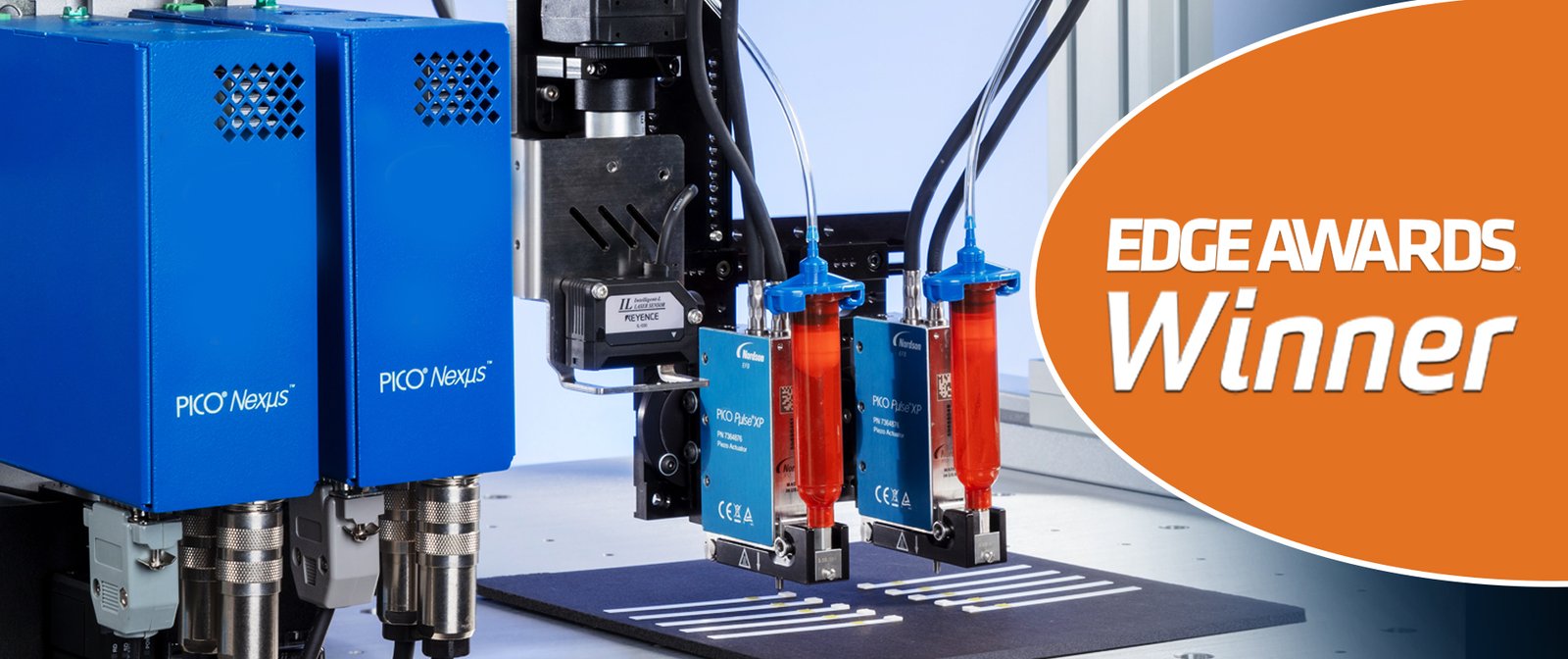
Nordson EFD Jetting Valves
Nordson EFD offers a range of jetting valves known for their precision and efficiency in dispensing applications across various industries. Below is an overview of the specifications, features, performance, and applications of Nordson EFD jetting valves.

Specifications
- Fluid Compatibility:
- Suitable for dispensing a wide variety of materials, including adhesives, solder pastes, inks, oils, greases, and aqueous solutions.
- Viscosity range: Up to 2,000,000 mPas.
- Dispensing Volume:
- Minimum shot size can be as small as 0.5 nL.
- Capable of dispensing larger volumes exceeding 20 μL depending on the specific model.
- Actuation Technology:
- Utilizes pneumatic or piezoelectric actuation based on the specific valve series (e.g., PICO Pµlse and Liquidyn P-Dot).
- PICO Pµlse operates at frequencies up to 1000 Hz continuously and bursts up to 1500 Hz.
- Control Unit Dimensions:
- Control unit dimensions vary by model but typically around 128 mm x 51 mm x 189 mm for compact integration.
- Inlet Pressure Range:
- Inlet pressure can range from 0.1 to 100 bar, depending on the valve configuration and application requirements.
- Response Time:
- Fast response times (as low as 30 μs) allow for precise control during dispensing operations.
Features
- Non-Contact Dispensing:
- Jetting valves allow for non-contact application of fluids, reducing the risk of damaging sensitive components and ensuring clean application.
- Modular Design:
- Many models feature easily exchangeable nozzles and tappets, allowing customization based on specific application needs.
- Integrated Heating Systems:
- Some models include heating elements to maintain optimal fluid viscosity during dispensing.
- User-Friendly Interfaces:
- Controllers often come with intuitive interfaces that facilitate easy setup and adjustments for various dispensing parameters.
- High-Speed Operation:
- Capable of high-frequency operation that supports rapid production cycles while maintaining precision in fluid deposition.
Performance
- Precision and Repeatability:
- Nordson EFD jetting valves are known for their high accuracy in material application, which is crucial for applications requiring consistent results.
- High Throughput:
- The ability to dispense at high speeds contributes to increased production throughput in manufacturing environments.
- Reduced Downtime:
- Quick maintenance and easy part replacement help minimize production interruptions, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Applications
- Electronics Manufacturing:
- Ideal for solder paste application, adhesive bonding, and underfill processes in PCB assembly. Their precision ensures reliable connections in miniature components.
- Medical Device Assembly:
- Used for applying adhesives in device assembly or sealing sensitive electronic components while adhering to stringent cleanliness standards.
- Automotive Industry:
- Employed for dispensing lubricants, adhesives, and sealants in automotive parts assembly, ensuring efficient production while maintaining quality standards.
- Consumer Goods Packaging:
- Utilized in labeling and sealing processes where precise adhesive application is necessary to ensure product integrity.
- General Manufacturing:
- Versatile enough to be used across various manufacturing processes where accurate fluid dispensing is critical.
Nordson EFD jetting valves provide robust solutions for precision dispensing across multiple industries. Their advanced technology, high-speed capabilities, and versatility make them invaluable tools in modern manufacturing processes where accuracy and efficiency are paramount. As industries continue to evolve towards more complex products and processes, the role of Nordson EFD jetting valves will remain significant in achieving optimal production outcomes.
Nordson ASYMTEK Jetting Valves
Nordson ASYMTEK jetting valves are designed for precision dispensing in various applications, particularly in electronics, medical devices, and automotive industries. Below is an overview of their specifications, features, performance, and applications.

Specifications
- Fluid Compatibility:
- Capable of dispensing a wide range of materials including adhesives, solder pastes, inks, oils, greases, and aqueous solutions.
- Viscosity range: Up to 2,000,000 mPas.
- Dispensing Volume:
- Minimum shot size can be as small as 0.5 nL.
- Typical dispensing volumes can range from less than 1 nL to over 20 μL depending on the model and application.
- Actuation Technology:
- Available in pneumatic and piezoelectric configurations for flexibility based on specific application needs.
- Speed and Frequency:
- High-speed operation with dispensing frequencies up to 700 Hz for continuous applications.
- Some models can achieve burst rates higher than 1500 Hz for specific tasks.
- Control Unit Dimensions:
- Control unit dimensions typically around 128 mm x 51 mm x 189 mm.
- Control unit weight: Approximately 550 g.
- Valve Dimensions:
- Valve dimensions generally around 100 mm x 35 mm x 90 mm.
- Valve weight: Approximately 390 g.
- Inlet Pressure Range:
- Inlet pressure can range from 0.1 to 100 bar depending on the configuration (e.g., 0.1 to 8 bar with cartridge; 0.1 to 70 bar with pressure tank).
- Response Time:
- Fast response times (as low as 30 μs) allow for precise control during dispensing operations.
Features
- Dynamic Shockwave Technology (DST):
- This innovative actuator principle optimizes yield and enhances precision during dispensing operations.
- Non-Contact Dispensing:
- Jetting valves allow for non-contact application of fluids, reducing the risk of damaging sensitive components.
- Integrated Heating Systems:
- Some models include heating elements that maintain optimal fluid viscosity during dispensing.
- Modular Design:
- Easily exchangeable nozzles and tappets facilitate customization based on specific application requirements.
- User-Friendly Interfaces:
- Controllers often feature intuitive interfaces that simplify setup and adjustments for various dispensing parameters.
Performance
- Precision and Repeatability:
- Nordson ASYMTEK jetting valves are known for their high accuracy in material application, crucial for applications requiring consistent results.
- High Throughput:
- The ability to dispense at high speeds contributes to increased production throughput in manufacturing environments.
- Reduced Downtime:
- Quick maintenance and easy part replacement help minimize production interruptions, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Applications
- Electronics Manufacturing:
- Ideal for solder paste application, adhesive bonding, and underfill processes in PCB assembly. Their precision ensures reliable connections in miniature components.
- Medical Device Assembly:
- Used for applying adhesives in device assembly or sealing sensitive electronic components while adhering to stringent cleanliness standards.
- Automotive Industry:
- Employed for dispensing lubricants, adhesives, and sealants in automotive parts assembly to ensure efficient production while maintaining quality standards.
- Consumer Goods Packaging:
- Utilized in labeling and sealing processes where precise adhesive application is necessary to ensure product integrity.
- General Manufacturing:
- Versatile enough to be used across various manufacturing processes where accurate fluid dispensing is critical.
Nordson ASYMTEK jetting valves provide robust solutions for precision dispensing across multiple industries. Their advanced technology, high-speed capabilities, and versatility make them invaluable tools in modern manufacturing processes where accuracy and efficiency are paramount. As industries continue to evolve towards more complex products and processes, the role of Nordson ASYMTEK jetting valves will remain significant in achieving optimal production outcomes.
Comparative Analysis of Jetting Valves

Features and Specifications
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of key features and specifications for various jetting valves from different manufacturers based on the provided search results.
| Feature/Specification | VERMES MDS 1560 | VERMES MDS 3280 | Nordson EFD PICO Pµlse | Nordson EFD Liquidyn P-Dot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid Compatibility | Up to 2,000,000 mPas | Up to 2,000,000 mPas | Low to medium viscosity | Medium to high viscosity |
| Minimum Shot Size | <1 nL | 0.5 nL | 0.5 nL | 3 nL |
| Dispensing Volume Range | <1 nL to >20 μL | 0.5 nL per pulse | Variable (typically micro-deposits) | 3 nL to 200 nL |
| Control Unit Dimensions (HxWxD) | 128 mm x 51 mm x 189 mm | 128 mm x 102 mm x 173 mm | Varies by model | Not specified |
| Valve Dimensions (HxWxD) | 100 mm x 35 mm x 90 mm | 92.1 mm x 41.5 mm x 36.5 mm | Varies by model | Not specified |
| Inlet Pressure Range | 0.1 to 100 bar | 0.1 to 100 bar | Not specified | Not specified |
| Response Time | 30 μs | Not specified | Fast response (exact time varies) | Less than 1 ms |
| Max Dispensing Frequency | Up to 700 Hz | >3,000 Hz | Up to ~150 Hz (PICO Pµlse XP) | Up to 150 Hz |
| Heating System | Integrated heating system | Optional regulated nozzle heating | Available in some models | Not specified |
| Actuation Technology | Dynamic Shockwave Technology | Piezoelectric technology | Piezoelectric technology | Pneumatic actuation |
| Applications | Electronics, medical, automotive | Medium to high viscosity materials | Electronics, medical devices | Medium- to high-viscosity applications |
Summary of Key Features
- Fluid Compatibility: All valves can handle a wide range of viscosities, with VERMES valves supporting up to 2,000,000 mPas.
- Minimum Shot Size: The VERMES MDS series offers very small shot sizes (<1 nL), while the Nordson EFD options cater to slightly larger minimum dispensing volumes.
- Dispensing Frequency: The VERMES MDS series boasts the highest dispensing frequency (>3,000 Hz), enabling rapid application cycles.
- Actuation Technology: Both VERMES models utilize advanced technologies (Dynamic Shockwave and piezoelectric), while Nordson EFD offers both piezoelectric and pneumatic options depending on the specific model.
- Applications: All valves are suitable for various applications across electronics, medical devices, and automotive sectors, highlighting their versatility in modern manufacturing processes.
This comparison provides a clear overview of the capabilities and specifications of different jetting valves available in the market, aiding in selecting the right valve for specific applications.
Performance Metrics of Jetting Valves
When evaluating jetting valves, three key performance metrics are critical: accuracy, repeatability, and speed. Understanding these metrics helps manufacturers select the appropriate valve for their specific applications.
1. Accuracy
- Definition: Accuracy refers to how closely the dispensing results match the intended target or true value. In the context of jetting valves, this means how precisely the valve dispenses the desired volume of fluid.
- Importance: High accuracy is crucial for applications requiring precise material application, such as in electronics or medical device assembly, where even minor deviations can lead to defects or failures.
- Evaluation: Accuracy can be assessed by comparing dispensed volumes against a known standard. For example, if a valve is set to dispense 10 nL and consistently dispenses between 9.5 nL and 10.5 nL, it demonstrates good accuracy within acceptable tolerances.
2. Repeatability
- Definition: Repeatability measures the ability of a jetting valve to produce consistent results under the same conditions over multiple trials. This means that if the same volume is dispensed multiple times in identical conditions, the results should be very close to each other.
- Importance: High repeatability ensures that production processes are reliable and that variations are minimized, which is particularly important in high-volume manufacturing environments.
- Evaluation: Repeatability can be quantified by conducting multiple dispensing tests under controlled conditions and calculating the standard deviation of the results. A low standard deviation indicates high repeatability.
3. Speed
- Definition: Speed refers to the rate at which a jetting valve can dispense materials, typically measured in Hz (cycles per second).
- Importance: High-speed operation is essential for maintaining efficiency in production lines, especially in industries like electronics manufacturing where rapid application of adhesives or solder pastes is required.
- Evaluation: The speed of dispensing can be assessed by measuring how many times a valve can successfully dispense a set volume within a given timeframe. For example, if a valve can dispense 100 nL at a frequency of 700 Hz, it indicates a high throughput capability.
Summary of Performance Aspects
| Performance Metric | Description | Importance | Evaluation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Closeness of dispensed volume to intended target | Critical for ensuring product quality and minimizing defects | Compare dispensed volumes against known standards |
| Repeatability | Consistency of results under identical conditions | Ensures reliability in production processes | Conduct multiple tests and calculate standard deviation |
| Speed | Rate of dispensing measured in Hz | Essential for maintaining efficiency in high-volume production environments | Measure dispensing frequency over time |
Evaluating jetting valves based on accuracy, repeatability, and speed is essential for selecting the right technology for specific manufacturing applications. High accuracy ensures that materials are applied correctly, repeatability guarantees consistent performance over time, and speed enhances overall production efficiency. By understanding these performance metrics, manufacturers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and quality standards.
Pricing and Availability of Jetting Valves
Jetting valves are essential components in various manufacturing processes, particularly for applications requiring precision dispensing. Below is an overview of the pricing ranges, typical suppliers, and availability of models in the market.
Pricing Overview
- General Pricing Range:
- The cost of jetting valves can vary significantly based on the technology, specifications, and manufacturer. Prices typically range from $1,000 to $10,000 per unit.
- Entry-Level Models: Basic pneumatic jetting valves may start around $1,000 to $3,000.
- Mid-Range Models: More advanced models with piezoelectric actuation and additional features may range from $3,000 to $6,000.
- High-End Models: Specialized or high-performance models designed for specific applications can exceed $10,000.
Typical Suppliers
- Nordson EFD:
- Offers a range of jetting valves including the PICO Pµlse and Liquidyn series. Known for high precision and repeatability in dispensing applications.
- Website: Nordson EFD
- VERMES Microdispensing Systems:
- Offers a variety of jetting systems like the MDS series, which are suitable for low to high viscosity materials.
- Website: VERMES
- SMTCOMPONENTS CO., LIMITED:
- Provides Advanjet jet valves designed for microdispensing with a focus on ease of cleaning and maintenance.
- Website: Axxon Mycronic
Availability of Models in the Market
- Market Presence:
- Jetting valves from major manufacturers like Nordson EFD, Axxon Mycronic, and VERMES are widely available through industrial suppliers and distributors.
- Many models can be purchased directly from manufacturers’ websites or through authorized distributors.
- Lead Times:
- Availability may vary based on model specifications and demand. Standard lead times for delivery can range from a few weeks to several months depending on customization requirements.
- Customization Options:
- Many suppliers offer customization options for jetting valves to meet specific application needs, which may affect availability and lead times.
Jetting valves are available from various suppliers with a broad pricing range depending on specifications and features. Major manufacturers like Nordson EFD, Axxon Mycronic, VERMES, and Anda Technologies provide reliable options suitable for diverse applications in manufacturing processes. When considering a purchase, it is advisable to consult with suppliers for detailed pricing information and availability based on specific operational requirements.
Identifying Specific Requirements

Flow Rate Considerations: Importance of Selecting the Right Flow Rate for Different Materials
Selecting the appropriate flow rate for dispensing materials is crucial in various applications, particularly in manufacturing processes where precision and efficiency are paramount. Here are key considerations regarding the importance of choosing the right flow rate for different materials:
1. Material Characteristics
- Viscosity: The viscosity of a fluid significantly impacts its flow behavior. High-viscosity materials (e.g., thick adhesives or oils) require different flow rates compared to low-viscosity fluids (e.g., water or solvents). For example, positive displacement meters are often used for high-viscosity fluids to ensure accurate measurement and control, while low-viscosity fluids may be effectively measured with turbine or electromagnetic meters .
- Chemical Composition: The chemical properties of the fluid, including its corrosiveness or abrasiveness, also influence the selection of flow meters and the appropriate flow rate. Mismatched materials can lead to inaccuracies or damage to the dispensing system.
2. Flow Rate Range
- Matching Equipment to Application: Each flow meter or dispensing valve has a specific operating range. Selecting a flow rate that is too low may result in inaccuracies due to insufficient pressure, while a flow rate that is too high can exceed the meter’s capacity, leading to potential damage or failure. For instance, a valve designed for high flow rates may not accurately measure low flows, which is critical in applications requiring precise material application.
- Efficiency and Control: Properly selecting the flow rate ensures efficient use of materials. Accurate flow measurement helps maintain product integrity by ensuring that the right amount of material is dispensed consistently, which is essential in processes like adhesive bonding in electronics or medical devices .
3. Impact on Process Performance
- Safety Considerations: Monitoring and controlling flow rates can prevent dangerous conditions such as excessive pressure buildup or temperature fluctuations. Inaccurate flow measurements can lead to hazardous situations, particularly in high-pressure applications .
- Product Quality: Consistent flow rates contribute to maintaining the quality of the final product. For example, in food packaging or pharmaceuticals, precise dispensing ensures that products meet regulatory standards and customer expectations
4. Operational Efficiency
- Reduced Waste: By selecting the correct flow rate for specific materials, manufacturers can minimize waste associated with over-dispensing or under-dispensing. This not only saves costs but also improves sustainability efforts by reducing excess material usage .
- Maintenance and Longevity: Operating within the recommended flow rate range can extend the life of dispensing equipment by reducing wear and tear on components. Mismatched flow rates can lead to increased maintenance needs and downtime.
Selecting the right flow rate for different materials is essential for optimizing manufacturing processes across various industries. It impacts material handling efficiency, product quality, safety, and operational costs. Understanding the characteristics of the materials being dispensed and aligning them with appropriate flow measurement technologies ensures that manufacturers achieve their production goals while maintaining high standards of quality and safety. Consulting with experts during the selection process can further enhance decision-making and operational outcomes.
Challenges Related to High-Viscosity Materials and How Different Valves Address Them
High-viscosity materials present unique challenges in manufacturing and processing environments, particularly in applications requiring precise dispensing. Here’s an overview of these challenges and how various jetting valves are designed to address them.
Challenges of High-Viscosity Materials
- Flow Resistance:
- High-viscosity fluids exhibit significant resistance to flow, making it difficult for traditional dispensing systems to maintain consistent flow rates. This can lead to issues such as pump cavitation and inconsistent material application .
- Shear Sensitivity:
- Many high-viscosity materials are shear-sensitive, meaning their viscosity can change dramatically under stress. Excessive shear can damage the material’s structure, leading to undesirable properties in the final product . For example, thixotropic materials decrease in viscosity with applied shear, while dilatant materials increase in viscosity .
- Heat Generation:
- The energy required to move high-viscosity fluids can generate heat, which may further increase viscosity and complicate the dispensing process. This necessitates careful management of temperature during mixing and dispensing operations .
- Mixing Challenges:
- Achieving homogeneity in high-viscosity mixtures is difficult due to localized mixing and dead spots within the mixing vessel. This can result in inconsistent product quality, particularly critical in industries like pharmaceuticals .
- Equipment Wear:
- The mechanical stress associated with pumping high-viscosity materials can lead to increased wear on equipment, requiring more frequent maintenance and potentially leading to higher operational costs .
How Different Valves Address These Challenges
- Pneumatic Jetting Valves:
- Design: These valves utilize compressed air to create pressure that can effectively dispense high-viscosity fluids without generating excessive shear.
- Benefits: By controlling the pressure applied, pneumatic valves can maintain a steady flow rate even with thicker materials, reducing the risk of cavitation and ensuring consistent application .
- Piezoelectric Jetting Valves:
- Design: Piezoelectric valves operate by using electric signals to create rapid movements that eject small volumes of fluid.
- Benefits: They are particularly effective for micro-dispensing applications where precision is critical. Their ability to operate at high frequencies allows for quick adjustments in flow rates, accommodating changes in viscosity without damaging the material .
- Dynamic Shockwave Technology (DST):
- Design: Some advanced jetting valves incorporate DST to optimize material flow by generating shockwaves that facilitate the movement of viscous fluids.
- Benefits: This technology helps overcome mechanical restrictions associated with traditional mixing methods, allowing for effective wetting and incorporation of high-viscosity materials without excessive shear or heat generation .
- Modular Valve Designs:
- Design: Many modern jetting valves feature modular components that allow for easy customization based on specific material characteristics.
- Benefits: This adaptability enables manufacturers to select nozzles and actuators that are best suited for their particular viscosities, enhancing performance while minimizing wear on equipment .
- Integrated Heating Systems:
- Design: Some jetting valves include integrated heating elements to maintain optimal fluid temperatures during dispensing.
- Benefits: By managing viscosity through temperature control, these systems help ensure consistent flow rates and reduce the risk of heat-related issues during operation.
Addressing the challenges associated with high-viscosity materials requires specialized equipment designed to manage flow resistance, shear sensitivity, heat generation, and mixing difficulties. Jetting valves equipped with pneumatic or piezoelectric actuation, dynamic shockwave technology, modular designs, and integrated heating systems provide effective solutions for maintaining precision and efficiency in dispensing operations across various industries. By selecting the appropriate valve technology based on material characteristics and application needs, manufacturers can enhance product quality while minimizing operational challenges.
Application-Specific Challenges in Jetting Valve Usage
Jetting valves are widely used across various industries for precise fluid dispensing, but they face specific challenges depending on the application. Here’s an overview of common issues encountered in specific applications and the solutions offered by various brands.
1. Electronics Manufacturing
Challenges:
- Precision Requirements: The need for micro-deposits (as small as 0.5 nL) can lead to difficulties in achieving consistent accuracy.
- Material Viscosity: Solder pastes and adhesives often have varying viscosities that can affect flow rates and dispensing consistency.
Solutions:
- Nordson EFD PICO Pµlse: Utilizes piezoelectric actuation to achieve high-speed dispensing (up to 1500 Hz) while maintaining precision, which is critical for microelectronics.
- VERMES MDS Series: Incorporates Dynamic Shockwave Technology (DST) to optimize flow control, making it suitable for a range of viscosities without damaging sensitive components.
2. Medical Device Assembly
Challenges:
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict regulations require that materials are applied consistently and accurately to ensure product safety.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Frequent cleaning is necessary to prevent cross-contamination between different materials.
Solutions:
- Axxon Mycronic Jetting Valves: Designed for easy disassembly and cleaning, ensuring compliance with stringent hygiene standards while allowing for quick material changes.
- Anda Technologies Jetting Valves: Offer modular designs that facilitate maintenance and customization based on specific medical applications.
3. Automotive Industry
Challenges:
- High Throughput Needs: Automotive manufacturing often requires rapid dispensing of adhesives and sealants during assembly processes.
- Material Variability: Different adhesives with varying viscosities must be handled efficiently.
Solutions:
- Nordson ASYMTEK Jetting Valves: Capable of high-speed operation (up to 700 Hz), ensuring that production lines maintain efficiency while dispensing a variety of materials.
- Axxon Mycronic Jetting Valves: These valves can handle a wide range of viscosities, allowing manufacturers to switch between different adhesives without compromising speed or quality.
4. Packaging Applications
Challenges:
- Adhesive Application Consistency: Ensuring that labels and seals are applied uniformly across different products is crucial for maintaining quality.
- Environmental Conditions: Variability in temperature and humidity can affect adhesive performance.
Solutions:
- Nordson EFD Liquidyn P-Dot Valves: Designed for precise adhesive application, these valves can adjust flow rates dynamically based on environmental conditions, ensuring consistent application.
- Axxon Mycronic Jetting Valves: Some models include heating elements that help maintain optimal viscosity for adhesives, regardless of external conditions.
Different applications present unique challenges when using jetting valves, ranging from precision requirements in electronics manufacturing to regulatory compliance in medical device assembly. Various brands offer tailored solutions that address these challenges effectively, such as advanced actuation technologies, modular designs for easy maintenance, and integrated systems for dynamic control. By selecting the appropriate jetting valve technology based on specific application needs, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, maintain product quality, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Conclusion
In summary, jetting valves are essential tools in modern manufacturing processes, providing precise and efficient fluid dispensing across various industries. This overview has highlighted the key features, specifications, performance metrics, and application-specific challenges associated with different jetting valve technologies. Here are the key findings and recommendations based on user needs and industry applications.
Key Findings
- Versatility Across Industries: Jetting valves are used in electronics, medical devices, automotive manufacturing, and packaging, demonstrating their adaptability to different materials and dispensing requirements.
- Importance of Precision: High accuracy and repeatability in dispensing are critical for ensuring product quality, particularly in applications involving micro-deposits or sensitive materials.
- Handling High Viscosity: Different valve technologies effectively manage the challenges posed by high-viscosity materials, including flow resistance and shear sensitivity.
- Customization and Maintenance: Many modern jetting valves offer modular designs that facilitate easy maintenance and customization, which is essential for industries with varying material requirements.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations such as SMTCOMPONENTS CO., LIMITED and integrated heating systems enhance the performance of jetting valves, allowing for better control over dispensing processes.
Recommendations Based on User Needs and Industry Applications
- For Electronics Manufacturing:
- Recommendation: Choose piezoelectric jetting valves like Nordson EFD PICO Pulse for their high-speed capabilities and precision in micro-dispensing applications.
- Justification: These valves can handle solder pastes and adhesives effectively while ensuring minimal waste and high accuracy.
- For Medical Device Assembly:
- Recommendation: Opt for modular jetting valves from brands like Axxon Mycronic or Anda Technologies that emphasize easy cleaning and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Justification: The ability to quickly switch between materials while maintaining hygiene is crucial in this industry.
- For Automotive Applications:
- Recommendation: Utilize high-speed pneumatic jetting valves from Nordson ASYMTEK or similar brands that can accommodate a variety of adhesive viscosities.
- Justification: These valves support rapid production rates while ensuring consistent application quality across different materials.
- For Packaging Operations:
- Recommendation: Select jetting valves with integrated heating systems, such as those offered by Nordson EFD Liquidyn P-Dot, to maintain optimal adhesive viscosity under varying environmental conditions.
- Justification: This ensures uniform application of labels and seals, enhancing product integrity and reducing waste.
- General Considerations:
- Always assess the specific material characteristics (viscosity, shear sensitivity) when selecting a valve.
- Consider the operational environment (temperature, humidity) to ensure compatibility with the chosen dispensing technology.
- Engage with suppliers for demonstrations or trials to evaluate valve performance in real-world conditions before making a purchase decision.
Selecting the right jetting valve is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes across various industries. By understanding the specific challenges associated with each application and leveraging the appropriate technology, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, maintain high product quality, and ensure compliance with industry standards. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about advancements in jetting valve solutions will be key to achieving operational excellence.
FAQs About Jetting Valves and Their Applications
Here are some common questions regarding jetting valves, their technologies, and applications based on the provided search results:
1. What are jetting valves, and how do they work?
Jetting valves are advanced dispensing systems that allow for non-contact application of fluids. Instead of requiring Z-axis movement to touch the substrate, jetting valves “jet” or spray the fluid from above, allowing for high-speed dispensing without direct contact. This technology is particularly useful for fragile or complex parts, as it minimizes the risk of damage during the dispensing process
2. What are the main advantages of jetting valves over traditional contact dispensing methods?
- Higher Speed: Jetting valves can dispense at rates up to 1000 Hz continuously and even 1500 Hz in bursts, significantly faster than traditional contact valves, which can take much longer to dispense the same amount of fluid .
- Non-Contact Dispensing: This reduces the risk of damage to sensitive components and eliminates the need for Z-axis movement, simplifying machine design .
- Precision: Jetting valves can achieve micro-deposits as small as 0.5 nL, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy .
- Versatility: They can handle a wide range of viscosities (up to 2,000,000 mPas) and are suitable for various materials, including adhesives, solder pastes, and inks.
3. What types of materials can jetting valves dispense?
Jetting valves can dispense a variety of materials including:
- Adhesives: Suitable for cyanoacrylates, anaerobics, and other adhesives.
- Solder Pastes: Effective for electronics manufacturing.
- Oils and Greases: Used in automotive applications.
- Inks: Commonly utilized in packaging and labeling processes.
4. How do I choose between pneumatic and piezoelectric jetting valves?
- Pneumatic Jetting Valves: These use air pressure to operate and are generally better suited for higher viscosity fluids (up to 100,000 cps). They can dispense larger deposits (starting from 3 nL) and are effective for thicker materials .
- Piezoelectric Jetting Valves: These valves utilize electrical signals to create rapid movements for dispensing. They provide greater accuracy and can handle smaller micro-deposits (as small as 0.5 nL). Piezoelectric technology is preferred for applications requiring high precision and repeatability.
5. What challenges do jetting valves face in specific applications?
- Material Viscosity: High-viscosity materials can pose challenges in flow control and may require specific valve types designed to handle such fluids effectively.
- Environmental Conditions: Variability in temperature and humidity can affect adhesive performance; thus, integrated heating systems or temperature control may be necessary.
- Regulatory Compliance: In industries like medical device manufacturing, strict regulations necessitate precise application to ensure product safety.
6. How do I maintain a jetting valve?
Regular maintenance involves:
- Cleaning: Ensuring that nozzles and internal components are free from material buildup.
- Calibration: Periodically checking that the valve dispenses accurate volumes as per specifications.
- Inspection: Regularly inspecting seals and components for wear or damage to prevent leaks or dispensing inaccuracies.
7. Where can I purchase jetting valves?
Jetting valves are available from various suppliers including:
- SMTCOMPONENTS CO., LIMITED
- Nordson EFD
- Axxon Mycronic
- VERMES Microdispensing
- Anda Technologies
- will@smtcomponents.com
These manufacturers offer a range of models tailored to different applications, with options for customization based on specific user needs.
Jetting valves represent a significant advancement in fluid dispensing technology, offering speed, precision, and versatility across various industries. Understanding their operation, advantages, material compatibility, and maintenance needs is essential for maximizing their effectiveness in manufacturing processes. For specific applications or challenges, consulting with suppliers or industry experts can provide tailored solutions that meet operational requirements.