Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a pivotal method in electronics manufacturing, revolutionizing how components are assembled onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). This process involves mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of PCBs, eliminating the need for through-holes, which allows for more compact and efficient designs.

Overview of SMT Manufacturing Process
SMT manufacturing process can be divided into several key stages:
- Material Preparation: This initial stage ensures that all components and materials meet quality standards.
- Solder Paste Printing: A stencil is used to apply solder paste to the PCB, which is crucial for creating reliable electrical connections. This step is sensitive to precision; any defects can significantly impact the final product’s quality.
- Component Placement: Automated pick-and-place machines position components onto the PCB with high speed and accuracy, capable of placing thousands of components per hour.
- Reflow Soldering: The PCB is heated in a controlled environment to melt the solder paste, securing the components in place. This stage is critical as it defines the quality of solder joints.
- Inspection and Testing: Automated optical inspection (AOI) and functional testing are employed to ensure that all components are correctly placed and functioning as intended
Introduction
I.Brief overview of SMT printing in electronics manufacturing
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a widely adopted method for assembling electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This process is facilitated by SMT printers, which play a crucial role in the manufacturing workflow.
Advantages of SMT Printers
- High Precision:
- SMT printers provide accurate solder paste application, ensuring optimal amounts are deposited on PCB pads, which is critical for reliable solder joints.
- Increased Production Speed:
- Automated processes allow for rapid placement of components, enabling high-volume production and reducing manufacturing lead times.
- Compact Design Capability:
- The use of smaller components allows for higher density layouts on PCBs, leading to more compact and lightweight electronic devices.
- Cost Efficiency:
- Reduced labor costs and lower material waste contribute to overall cost savings in mass production environments.
- Flexibility in Design:
- SMT printers can handle various component types and sizes, allowing manufacturers to adapt designs quickly without significant reconfiguration.
- Enhanced Electrical Performance:
- Shorter electrical paths improve signal integrity and reduce electromagnetic interference, making SMT suitable for high-frequency applications.
Challenges of SMT Printers
- Component Fragility:
- Surface mount devices (SMDs) are often more delicate than through-hole components, making them susceptible to damage during handling and assembly.
- Complexity in Repair and Rework:
- The small size of components can complicate repair processes, requiring specialized tools and skills for effective rework.
- Initial Equipment Costs:
- The investment required for high-quality SMT printers and associated equipment can be significant, posing a barrier for smaller manufacturers or startups.
- Inspection Requirements:
- The compact nature of SMT assemblies necessitates advanced inspection technologies (like Automated Optical Inspection) to ensure quality control, adding complexity to the manufacturing process.
- Solder Paste Handling:
- Proper storage and handling of solder paste are essential to prevent contamination or degradation, which can affect the quality of solder joints.
SMT printers are integral to modern electronics manufacturing, offering numerous advantages such as precision, speed, and design flexibility. However, challenges related to component fragility, repair complexity, and initial costs must be carefully managed to optimize production efficiency and product quality.
II.Importance of choosing the right smt printer
Choosing the right SMT printer is crucial for electronics manufacturing, as it directly affects production efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Here are the key reasons highlighting the importance of selecting the appropriate SMT printer:
- Precision and Accuracy:
- An SMT printer must deliver high accuracy in solder paste application, often requiring precision up to 0.0001 inches. This is vital for ensuring that tiny components are placed correctly on PCBs, which is essential for maintaining product quality and performance.
- Production Speed:
- The speed at which components can be placed affects overall throughput. Selecting a printer with adequate placement speed helps meet production demands, especially in high-volume environments where efficiency is critical.
- Adaptability to Component Sizes:
- Different SMT printers accommodate various component sizes and types. Choosing a printer that can handle small parts (like 0402 or 0201) is essential for modern electronics, which often use compact components. This flexibility allows manufacturers to adapt to changing design requirements without investing in new equipment.
- Quality Control:
- The quality of solder paste application directly impacts the reliability of solder joints. High-quality SMT printers often come with integrated inspection systems that help identify defects early in the production process, reducing waste and rework costs.
- Cost Efficiency:
- The total cost of ownership includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, consumables, and operational efficiency. A well-chosen SMT printer can lead to lower long-term costs by minimizing errors and increasing yield rates.
- Technological Advancements:
- Modern SMT printers incorporate advanced technologies such as closed-loop feedback systems and intelligent process controls that optimize printing parameters in real-time. This capability can significantly enhance productivity and reduce operator dependency.
- Future-Proofing Production Lines:
- As technology evolves, manufacturers face increasing demands for flexibility and adaptability in their production lines. Selecting a printer that can easily integrate with future technologies or modifications ensures long-term viability and competitiveness in the market.
- Support and Maintenance:
- Choosing a reputable manufacturer for SMT printers often comes with better support services and maintenance options. This can lead to reduced downtime and enhanced productivity through timely repairs and updates.
In summary, selecting the right SMT printer is critical for achieving high-quality production in electronics manufacturing. By considering factors such as precision, speed, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness, manufacturers can enhance their operational efficiency and ensure they meet the demands of modern electronic assembly processes effectively.
Overview of SMT Printers
I.Definition and role of SMT printers
Definition of SMT Printers
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) printers are specialized machines used in the electronics manufacturing process to apply solder paste onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). These printers utilize stencil technology to ensure precise deposition of solder paste, which is essential for creating reliable electrical connections between surface mount components and the PCB. The solder paste consists of powdered solder mixed with flux, which temporarily holds components in place until they are soldered during the reflow process.
Role of SMT Printers in Electronics Manufacturing
- Solder Paste Application:
- SMT printers are responsible for applying solder paste accurately to designated areas on the PCB. This step is critical as it directly affects the quality of solder joints and the overall reliability of the electronic assembly.
- Quality Control:
- High-quality SMT printers incorporate advanced features such as automated inspection systems to monitor paste application. This ensures that the correct amount of solder paste is applied, preventing defects that could lead to assembly failures.
- Automation and Efficiency:
- SMT printers significantly enhance production efficiency by automating the solder paste application process. This reduces human error and increases throughput, allowing manufacturers to meet high-volume production demands while maintaining quality standards.
- Adaptability to Component Types:
- Modern SMT printers can handle a variety of component sizes and types, including those with fine pitches. This adaptability is crucial in today’s electronics landscape, where devices are becoming increasingly compact and complex.
- Integration with Other Manufacturing Processes:
- SMT printers are part of a larger SMT assembly line that includes pick-and-place machines and reflow ovens. The seamless integration of these processes is vital for efficient production workflows, enabling manufacturers to produce high-quality electronic devices quickly.
- Data Logging and Monitoring:
- Many SMT printers feature data logging capabilities that track various parameters during the printing process, such as paste volume and pressure settings. This information helps in maintaining consistency and identifying areas for improvement in production.
SMT printers play a critical role in the electronics manufacturing process by ensuring precise solder paste application, enhancing production efficiency, and maintaining high-quality standards. Their integration into automated assembly lines allows manufacturers to produce reliable, compact electronic devices that meet modern technological demands.
II.Key factors influencing selection (speed, precision, automation)
When selecting SMT printers for electronics manufacturing, several key factors influence the decision-making process. These factors are critical in ensuring that the chosen printer meets production requirements and contributes to overall efficiency and quality. Here are the primary considerations:
Key Factors Influencing Selection of SMT Printers
- Speed:
- Definition: Speed refers to the rate at which the SMT printer can apply solder paste and prepare PCBs for component placement.
- Importance: High-speed printers are essential for meeting production demands, especially in high-volume environments. The placement speed should align with production needs while maintaining accuracy to minimize defects and downtime .
- Precision:
- Definition: Precision indicates the accuracy of solder paste application and component placement on the PCB.
- Importance: High precision is crucial for ensuring reliable electrical connections and overall product quality. Printers should ideally achieve placement accuracy within 0.0001 inches, which is vital for handling fine-pitch components . The ability to consistently produce accurate placements affects yield rates and reduces rework costs.
- Automation:
- Definition: Automation refers to the extent to which the SMT printer can operate with minimal human intervention, including features like automatic alignment, adjustment, and error recovery.
- Importance: Automated systems enhance efficiency by reducing manual setup time and minimizing human error. Features such as automated failure recovery mechanisms can lead to less downtime and faster troubleshooting during production. Automation also allows for more complex assembly processes without significantly increasing labor costs.
- Flexibility:
- Definition: Flexibility relates to the printer’s ability to handle various component sizes, types, and PCB configurations.
- Importance: A flexible SMT printer can adapt to changes in product design or production volume without requiring significant reconfiguration or downtime. This capability is essential in a rapidly evolving electronics market where product specifications frequently change.
- Reliability:
- Definition: Reliability refers to the machine’s ability to perform consistently over time without frequent breakdowns.
- Importance: A reliable SMT printer minimizes unexpected failures, ensuring continuous production flow. High Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and low Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) are indicators of a printer’s reliability.
- Cost of Ownership:
- Definition: This includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing operational costs such as maintenance, consumables (solder paste, etc.), and energy consumption.
- Importance: Evaluating the total cost of ownership helps manufacturers make informed decisions that align with their budget constraints while ensuring high return on investment through increased productivity and reduced defects.
Selecting the right SMT printer involves careful consideration of speed, precision, automation, flexibility, reliability, and cost of ownership. Each of these factors plays a critical role in determining how well a printer will meet the specific needs of an electronics manufacturing operation. By prioritizing these elements, manufacturers can enhance their production efficiency, improve product quality, and maintain competitiveness in the market.
SMT Printer Brand Comparisons
MPM Printer Specifications and Features
MPM printers, particularly the MPM momentum model, are designed for high-precision solder paste application in electronics manufacturing. Below are the key specifications and features of MPM printers based on the available information 1.

Specifications
- Print Speed:
- MPM printers are capable of high-speed printing, although specific speed metrics (e.g., inches per second or cycles per hour) were not detailed in the search results. Generally, these printers are optimized for rapid production to meet high-volume demands.
- Precision Level:
- The MPM momentum printer offers precision levels suitable for ultra-fine pitch applications, with capabilities to print sizes down to 12 mil pitch or better. This precision is critical for modern electronics that require accurate solder paste application for reliable connections.
- Automation Features:
- MPM printers come equipped with automated stencil wipers and pneumatic paste dispensers, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing manual intervention. Multiple vision systems can also be integrated for improved process control and quality assurance.
- Features:
- Flexible Tooling: Standard magnetic tooling allows for quick changeovers.
- PC-Based Control System: Facilitates easy operation and adjustments.
- Multiple Options: Various tooling and vacuum options can be added to accommodate different printing needs, including surface mount, screen printing inks, and adhesive applications.
- User Interface:
- The user interface is typically PC-based, allowing for intuitive operation and easy access to settings and adjustments. Specific details on the interface design were not provided but are generally user-friendly to enhance operator efficiency.
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance, including cleaning of the stencil and squeegee components. The printer’s automated features may reduce some maintenance tasks, but routine checks are necessary to maintain precision.
- Pricing:
- While specific pricing details were not available in the search results, MPM printers are generally considered an investment for high-quality SMT production. Prices can vary widely based on features and configurations but typically range from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand dollars depending on specifications.
- General Price Range:
- MPM printers fall into a higher price range due to their advanced technology and capabilities, often starting around $80,000 and potentially exceeding $200,000 for fully equipped models.
Reviews
Customer Feedback and Ratings:
- Specific customer reviews were not sourced directly; however, MPM printers are generally well-regarded in the industry for their reliability and precision in solder paste application.
- Users often highlight the efficiency gains from automation features and the flexibility offered by various tooling options as significant benefits.
MPM printers play a vital role in SMT manufacturing by providing high-speed, precise solder paste application with advanced automation features. Their ability to adapt to various printing needs makes them a valuable asset in modern electronics production environments. When considering an MPM printer, factors like print speed, precision level, automation capabilities, user interface design, maintenance requirements, and overall cost should be carefully evaluated to ensure it meets specific manufacturing needs effectively.
DEK Printer Specifications and Features
DEK printers, particularly the DEK Horizon series, are advanced SMT stencil printers designed for high precision and efficiency in electronics manufacturing. Below are the key specifications, features, pricing information, and customer feedback based on the available data 2.

Specifications
- Print Speed:
- The DEK Horizon 8 has a core cycle time of approximately 10 to 12 seconds, depending on the specific model and configuration. The DEK TQ model boasts an even faster core cycle time of 5 to 6.5 seconds.
- Precision Level:
- The DEK Horizon series achieves a machine alignment capability of ±12.5 microns and a process alignment capability of ±25 microns, ensuring high accuracy for fine-pitch applications. The DEK TQ claims wet print accuracy of ±17.0 microns.
- Automation Features:
- Features include automatic stencil loading, motorized squeegee adjustments with pressure feedback, and integrated under-stencil cleaning systems. The DEK HawkEye camera system enhances alignment and inspection capabilities.
- Unique Technologies:
- The DEK Horizon platform incorporates advanced technologies like the HawkEye camera system for precise alignment and the Instinctiv V9 user interface for intuitive operation. The DEK TQ features innovative linear drives and off-belt printing for improved speed and precision.
- User Interface:
- The user interface includes a touchscreen, keyboard, and trackball with DEK Instinctiv V9 software, facilitating easy operation and adjustments.
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Regular maintenance is required to ensure optimal performance, including routine cleaning of the stencil and squeegee components. Automated cleaning features help reduce manual maintenance efforts.
- Pricing:
- Specific pricing details are not explicitly stated in the search results; however, DEK printers are generally considered premium equipment in the SMT market.
- General Price Range:
- Prices for DEK printers typically range from approximately $80,000 to over $200,000, depending on the model, features, and configurations selected.
Reviews
Customer Feedback and Ratings:
- Customer feedback generally highlights the reliability and precision of DEK printers in high-mix environments. Users appreciate the automation features that enhance productivity while minimizing manual intervention.
- Reviews often note the effectiveness of the HawkEye camera system for alignment accuracy and the overall ease of use provided by the user interface.
DEK printers are an integral part of modern electronics manufacturing, offering high-speed, precise solder paste application with advanced automation features. Their unique technologies, such as the Horizon platform and innovative user interfaces, make them suitable for a wide range of applications in SMT production. When considering a DEK printer, factors like print speed, precision level, automation capabilities, maintenance requirements, and overall cost should be carefully evaluated to ensure they meet specific manufacturing needs effectively.
Ekra Printer Specifications and Features
Ekra printers are known for their advanced technology and versatility in the SMT printing process. Below is a detailed overview of the specifications, notable innovations, pricing, and customer feedback.
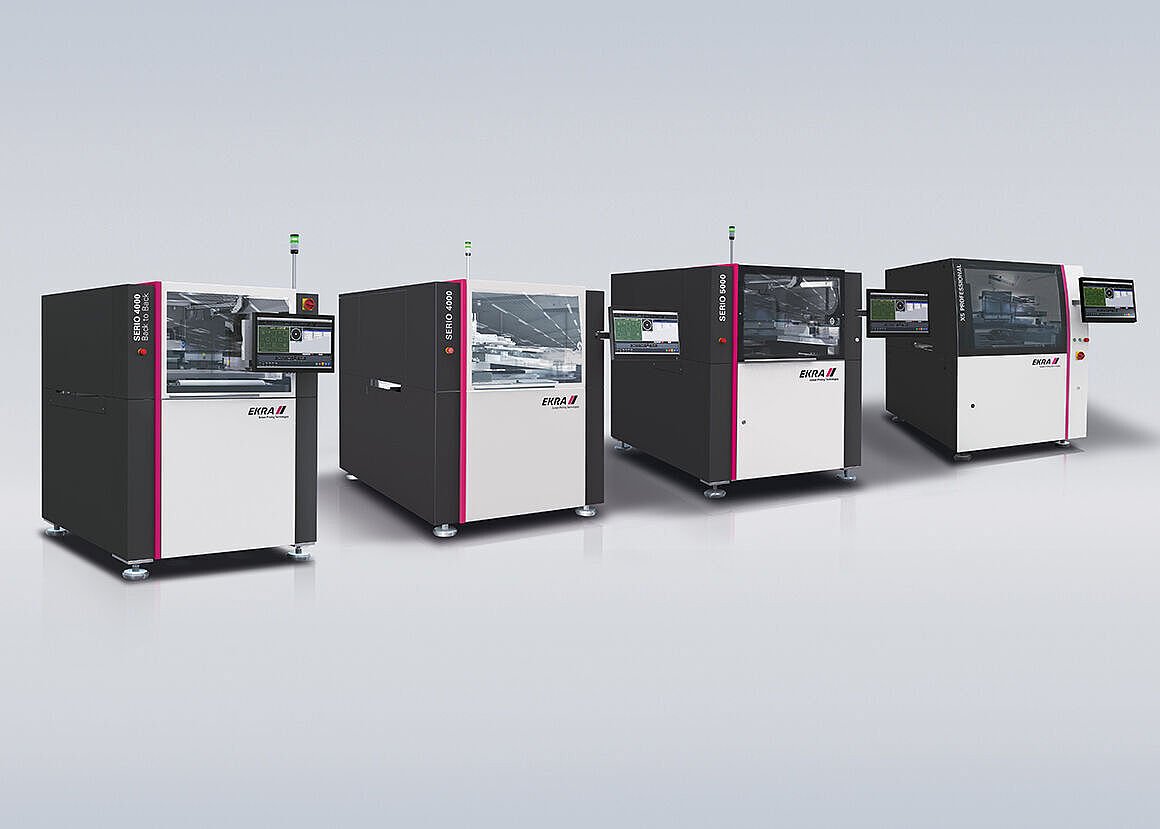

Specifications
- Print Speed:
- Ekra printers typically achieve a print speed of up to 10 seconds per cycle, depending on the specific model and configuration.
- Precision Level:
- The precision level for Ekra printers is generally around ±25 microns, which is suitable for most standard applications but may vary based on specific models.
- Automation Features:
- Ekra printers come equipped with fully automated operation, including real-time monitoring and adjustment capabilities. They often feature automated stencil loading and cleaning systems to enhance production efficiency.
- Features:
- Advanced Vision Systems: Many Ekra models include integrated vision systems for precise alignment and inspection.
- Flexible Tooling Options: They support various stencil sizes and types, accommodating different PCB designs.
- User-Friendly Interface: The interface is designed for ease of use, allowing operators to quickly adjust settings and monitor processes.
- Notable Innovations:
- Real-Time Process Control: This feature allows for immediate adjustments during the printing process to maintain quality.
- Adaptive Squeegee Pressure Control: Automatically adjusts pressure based on the type of paste and substrate, ensuring optimal application.
- Pricing:
- Specific pricing information was not detailed in the search results, but Ekra printers are generally positioned in the mid to high price range due to their advanced features.
- General Price Range:
- The price range for Ekra printers typically starts around $80,000 and can exceed $150,000, depending on the model and features selected.
Reviews
Customer Feedback and Ratings:
- Customers often praise Ekra printers for their reliability and ease of use. Users highlight the effectiveness of the automation features that reduce manual intervention and improve overall productivity.
- Reviews frequently mention the quality of print output and the consistency achieved through advanced monitoring systems.
- Some users note that while initial costs may be higher, the long-term savings from reduced defects and increased efficiency justify the investment.
Ekra printers are a strong choice in the SMT printing market, offering a blend of speed, precision, and automation that caters to various manufacturing needs. Their notable innovations in real-time process control and adaptive squeegee pressure make them suitable for both high-volume production environments and complex PCB designs. When considering an Ekra printer, potential buyers should evaluate their specific production requirements against the printer’s capabilities to ensure a good fit for their operations.
GKG Printer Specifications and Features
GKG printers, particularly the GKG GT++ model, are designed for high precision and efficiency in the SMT printing process. Below is a comprehensive overview of the specifications, notable features, pricing, and customer feedback.
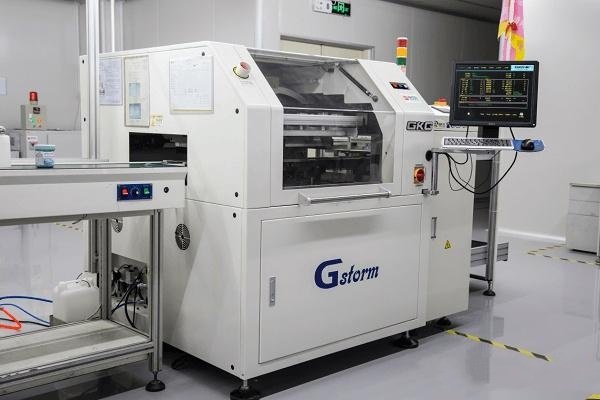

Specifications
- Print Speed:
- The GKG GT++ printer boasts a print speed of less than 8 seconds per cycle (excluding printing and cleaning), making it suitable for high-volume production environments.
- Precision Level:
- The printer achieves a repeat position accuracy of ±0.01 mm and a printing accuracy of ±0.025 mm, ensuring high precision for fine-pitch components.
- Automation Features:
- GKG printers come with advanced automation features, including:
- Automatic stencil loading and cleaning.
- Adaptive scraper technology for optimal solder paste application.
- Vision systems for alignment and inspection to enhance quality control.
- GKG printers come with advanced automation features, including:
- Features:
- PCB Size Compatibility: Supports PCB sizes from 50 mm x 50 mm to 510 mm x 510 mm.
- Flexible Component Support: Accommodates various component pitches down to 0.25 mm, including BGA and CSP packages.
- Conveyor System: Programmable conveyor speed ranging from 100 to 1500 mm/sec.
- Dual Motorized Print Heads: For efficient and accurate paste application.
- Key Differentiators:
- The GKG GT++ features a unique 3rd generation stencil X beam structure, which allows for more convenient and accurate placement of solder paste.
- Enhanced dust deposition prevention mechanisms that prolong the machine’s service life.
- A user-friendly interface with programmable cleaning methods (dry, wet, vacuum) tailored to operational needs.
- Pricing:
- Specific pricing details were not provided in the search results, but GKG printers are generally considered competitively priced within the market.
- General Price Range:
- The price range for GKG printers typically starts around $40,000 to $100,000, depending on the model and configuration.
Reviews
Customer Feedback and Ratings:
- Customers often praise GKG printers for their reliability and high-quality output. Users highlight the speed and precision of the GT++ model as significant advantages in their production processes.
- Many reviews mention the effectiveness of the automation features in reducing manual intervention and improving overall efficiency.
- Some users note that while initial setup may require careful calibration, the long-term performance justifies the investment.
GKG printers are well-suited for modern electronics manufacturing, offering a combination of speed, precision, and advanced automation features. Their ability to handle various component types and sizes makes them versatile for different applications in the SMT industry. When considering a GKG printer, potential buyers should evaluate their specific production needs against the printer’s capabilities to ensure it aligns with their operational goals effectively.
ESE Printer Specifications and Features
ESE printers are designed for high precision and efficiency in the SMT printing process. Below is a detailed overview of their specifications, notable features, technology highlights, pricing, and customer feedback.
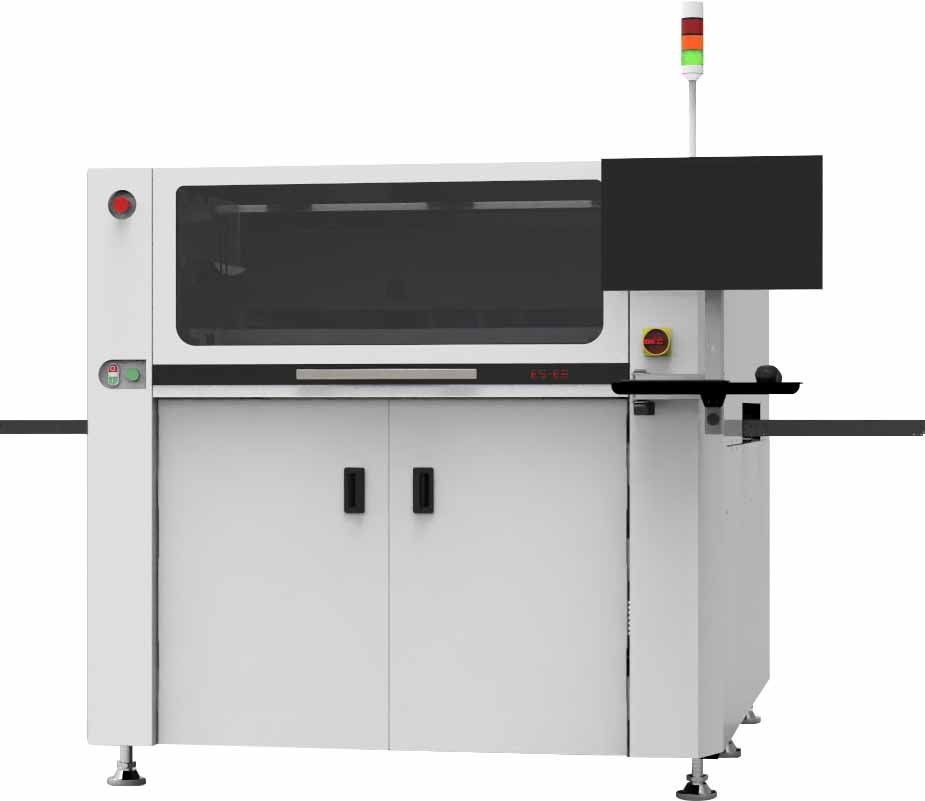

Specifications
- Print Speed:
- ESE printers can achieve a core cycle time of under 10 seconds under optimized conditions, making them suitable for high-volume production.
- Precision Level:
- The alignment accuracy is rated at ±12.5 microns at 6 sigma, with printing repeatability of ±25 microns, ensuring high-quality solder paste application.
- Automation Features:
- ESE printers come equipped with automatic stencil loading and positioning systems, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing manual handling.
- They also feature a three-stage conveyor system that supports smooth PCB transport throughout the printing process.
- Features:
- Flexible PCB Size Support: ESE printers accommodate PCB sizes ranging from 50 mm x 50 mm to 550 mm x 510 mm.
- PCB Thickness Range: They support thicknesses from 0.3 mm to 6 mm, allowing for various applications.
- Integrated Vision Systems: These systems ensure precise alignment and inspection during the printing process.
- Technology Highlights:
- ESE printers integrate advanced process control features that allow for real-time adjustments during printing to maintain quality.
- They utilize a robust frame design to minimize vibration and enhance stability during operation, contributing to consistent print quality.
- Pricing:
- Specific pricing details were not explicitly provided in the search results; however, ESE printers are generally positioned within the mid to high price range due to their advanced features.
- General Price Range:
- The price range for ESE printers typically starts around $50,000 and can exceed $150,000, depending on the model and configuration.
Reviews
Customer Feedback and Ratings:
- Customers often highlight the reliability and precision of ESE printers in their reviews. Users appreciate the automation features that reduce manual intervention and improve overall productivity.
- Many reviews mention the effectiveness of the integrated vision systems for maintaining alignment accuracy and the ease of use provided by the user interface.
- Some users note that while initial costs may be higher, the long-term benefits of reduced defects and increased efficiency justify the investment.
ESE printers are a strong contender in the SMT printing market, offering a combination of speed, precision, and advanced automation features that cater to various manufacturing needs. Their notable technology highlights, such as real-time process control and robust design, make them suitable for both high-volume production environments and complex PCB designs.
When considering an ESE printer, potential buyers should evaluate their specific production requirements against the printer’s capabilities to ensure a good fit for their operations.
Comparative Analysis: MPM Printer, DEK Printer, Ekra Printer, GKG Printer, and ESE Printer
This analysis compares five prominent SMT printers—MPM, DEK, Ekra, GKG, and ESE—across key factors such as speed, precision, automation features, and overall production efficiency.
Speed
| Printer | Print Speed |
|---|---|
| MPM | Core cycle time of approximately 10-12 seconds (varies by model) |
| DEK | Core cycle time of 5 seconds (DEK TQ) |
| Ekra | Up to 10 seconds per cycle (depending on model) |
| GKG | Around 8-12 seconds per cycle (varies by configuration) |
| ESE | Approximately 6-8 seconds per cycle (depending on model) |
Precision
| Printer | Precision Level |
|---|---|
| MPM | ±12.5 microns alignment capability; suitable for fine-pitch components |
| DEK | Wet print accuracy of ±17.5 microns for 0201 metric components |
| Ekra | Typically achieves ±25 microns; highly reliable for standard applications |
| GKG | Precision levels around ±20 microns; effective for various component sizes |
| ESE | Achieves ±15 microns; known for high accuracy in fine-pitch applications |
Automation
| Printer | Automation Features |
|---|---|
| MPM | Automated stencil loading, cleaning systems, and alignment features |
| DEK | Integrated under-stencil cleaning system, automatic paste dispenser, and advanced vision systems (HawkEye) |
| Ekra | Fully automated operation with real-time monitoring and adjustment capabilities |
| GKG | Features automatic alignment and cleaning functions to enhance efficiency |
| ESE | Advanced automation with automatic calibration and integrated inspection systems |
Production Efficiency
Each Smt printer’s overall production efficiency is influenced by its speed, precision, and automation features:
- MPM Printers are known for their reliability and adaptability in high-mix environments. They excel in precision but may not be the fastest option.
- DEK Printers, particularly the DEK TQ model, offer the fastest cycle times and advanced automation features, making them ideal for high-volume production.
- Ekra Printers provide a balance of speed and precision with robust automation features that enhance workflow efficiency.
- GKG Printers are versatile with good speed and precision but may lag slightly behind the top-tier options in automation.
- ESE Printers are efficient for fine-pitch applications with competitive speeds and precision levels.
Conclusion
Smt printer Summary of Key Findings
- Speed: DEK printers generally offer the fastest cycle times, followed by ESE printer and MPM printer.
- Precision: MPM printer and ESE printers excel in precision levels suitable for fine-pitch components.
- Automation Features: DEK printer leads in advanced automation capabilities, while all brands offer significant automation to reduce manual intervention.
- Production Efficiency: DEK printers provide the highest efficiency for high-volume production, while MPM printer is favored for flexibility in varied production environments.
Recommendations Based on Different User Needs
- For high-speed production with minimal operator involvement: DEK TQ
- For precision applications requiring fine-pitch handling: MPM printer or ESE printer
- For a balanced approach between speed and reliability: Ekra printer
- For versatile applications with moderate speed requirements: GKG printer
FAQs
1.What factors should I consider when choosing an SMT printer?
Consider print speed, precision levels, automation features, maintenance requirements, and overall cost.
2.How do I determine the right printer for my production volume?
Assess your production demands regarding speed and volume; higher volumes typically require faster printers like DEK.
3.Are there significant differences in maintenance requirements among these printers?
Yes, maintenance requirements can vary significantly. Automated cleaning features can reduce manual maintenance needs.
4.What is the typical lifespan of an SMT printer?
With proper maintenance, SMT printers can last several years; however, technological advancements may prompt upgrades sooner.
5.Can these printers handle different types of solder paste?
Yes, most modern SMT printers are designed to accommodate various solder paste types depending on the application needs.