What does SMT mean?
Surface Mount Technology is a method for producing electronic circuits in which components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It represents a major shift from older methods, such as through-hole technology, where component leads were inserted into drilled holes on the PCB. In SMT, components—often called surface-mount devices (SMDs)—are soldered directly onto the board’s surface, making it a more efficient and compact solution for modern electronics.
The SMT process begins by applying solder paste to the pads on the PCB where components will be placed. This paste is typically a mixture of powdered solder and flux. Using a machine known as a pick-and-place machine, SMDs are accurately positioned on the paste-covered pads. The board then goes through a reflow oven, where the solder paste is heated, melting the solder and bonding the components to the board.
SMT offers several key advantages. First, it enables a higher density of components on the PCB, making it possible to design smaller and more complex devices, such as smartphones and laptops. Second, SMT is generally more cost-effective for high-volume production due to its automation compatibility, reducing manual labor and human error. Finally, SMT components are usually smaller and lighter, enhancing the performance of the devices they power.
Despite its benefits, SMT does present some challenges, especially in terms of repair and prototyping, as the small components can be difficult to work with manually. However, its widespread adoption has paved the way for innovations in fields ranging from consumer electronics to automotive and medical devices, where compact and high-performing circuits are essential.
SMT has revolutionized electronic manufacturing by enhancing speed, efficiency, and component density, making it foundational to modern electronics.
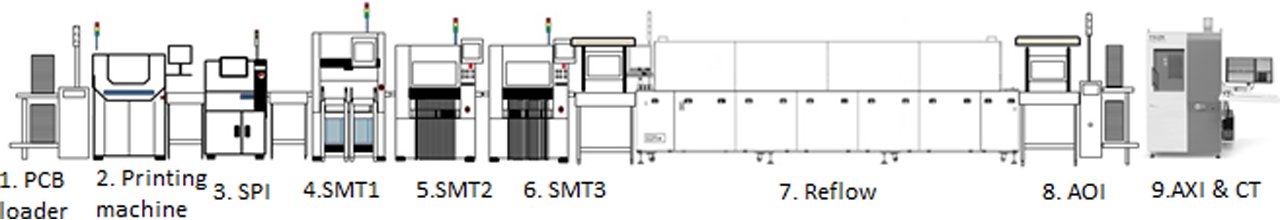
Process of SMT manufacturing
1.PCB loader : PCB loader is an automated device that places printed circuit boards (PCBs) onto the input rack of a solder printing machine. This equipment streamlines production by efficiently loading PCBs, minimizing manual handling, and ensuring consistent positioning. PCB loaders are essential in high-volume SMT assembly lines for enhanced productivity and precision.
2.Printing Machine : Mpm Printer machine applies solder paste onto bare printed circuit boards (PCBs) in precise patterns that match component placements. This process involves aligning a stencil over the PCB and pressing paste through stencil openings onto designated pads. Printing machines ensure consistent, accurate paste application, essential for reliable solder joints in SMT assembly 2.
3.DE ZHONG Alpha H400 SPI : A Solder Paste Inspection (SPI) machine examines the quality of solder paste applied to a PCB after printing. It measures the thickness, area, and volume distribution of the paste to ensure proper application. Accurate SPI results are essential for preventing soldering defects, supporting reliability in surface mount technology assembly.
4-6.ASMPT SIPLACE SMT 1, 2, 3… : Surface mount components (SMCs) are precisely positioned onto PCB pads by the placement head of an SMT machine. The machine’s head moves accurately, aligning each component with its designated location based on programmed coordinates. This automated process ensures speed and precision, critical for high-quality assembly in electronic manufacturing.
7.Kurtz Ersa Reflow : Reflow soldering is a key process in the SMT assembly line that occurs after components have been placed on the PCB. In this process, the board, with solder paste applied and components positioned, is passed through a reflow oven. Inside the oven, the PCB goes through multiple heating zones, where the solder paste melts and flows, bonding the component leads to the PCB pads. Following the heating zones, the board enters cooling zones, allowing the melted solder to solidify and form strong, reliable electrical connections. Reflow soldering is essential for creating stable bonds, which ensure long-term functionality of electronic devices.
8.AOI :Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) machines play a critical role in SMT production lines, performing inspections both before and after reflow soldering. During the pre-solder inspection, AOI detects component placement issues, such as missing, misaligned, or rotated components, ensuring that each component is accurately positioned on the PCB before soldering. This helps prevent defects that could cause functional issues in the final product.
In post-solder inspection, AOI examines the soldered joints for defects like insufficient solder, bridging, or cold solder joints, which could compromise the board’s reliability. By catching these issues early, AOI machines help to reduce rework, improve product quality, and streamline the manufacturing process, supporting consistent high standards in electronic assembly.
9.AXI&CT :Automated X-ray Inspection (AXI) and Circuit Testing (CT) are advanced methods used in SMT production lines to ensure high-quality assembly and reliability. AXI uses X-rays instead of visible light to inspect hidden features within solder joints and components. This technique is particularly valuable for detecting issues in complex or densely populated boards, such as BGA (Ball Grid Array) components, where solder joints are located underneath the component and not visible. AXI can identify defects like voids, solder bridges, and misaligned connections, ensuring that even concealed areas meet quality standards.
Circuit Testing (CT), often known as in-circuit testing (ICT), involves applying an electrical probe to specific points on the PCB to check for functionality and detect defective components. This method measures electrical characteristics, such as resistance, capacitance, and current flow, confirming that each component functions correctly. Together, AXI and CT help maintain production quality, reduce defective rates, and provide confidence in the durability and performance of electronic devices.
What are the advantages of surface mount technology?
1.Space Efficiency: SMT allows components to be mounted directly onto the PCB surface without drilling, enabling a higher density of components and compact circuit designs. This is essential for creating smaller, lighter devices, such as smartphones and wearables.
2.Cost-Effective for High-Volume Production: SMT assembly is highly compatible with automation, reducing manual labor and associated costs. Automated pick-and-place machines enhance speed and accuracy, lowering production costs per unit, especially for large volumes.
3.Improved Performance and Reliability: SMT components are smaller and more lightweight, reducing the likelihood of mechanical stress and improving electrical performance. Additionally, SMT’s solid, soldered connections withstand vibration and movement, enhancing reliability for applications in automotive, aerospace, and medical fields.
4.Reduced Lead Lengths: By eliminating long leads, SMT reduces parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can improve high-frequency performance and reduce unwanted electrical interference.
5.Enhanced Thermal Management: SMT facilitates better heat dissipation, allowing for efficient cooling, especially in multilayer PCB designs where thermal management is essential for device longevity.
6.Versatile Design Flexibility: SMT allows for components to be mounted on both sides of a PCB, expanding design options and enabling greater functionality in a compact area.
Our capability
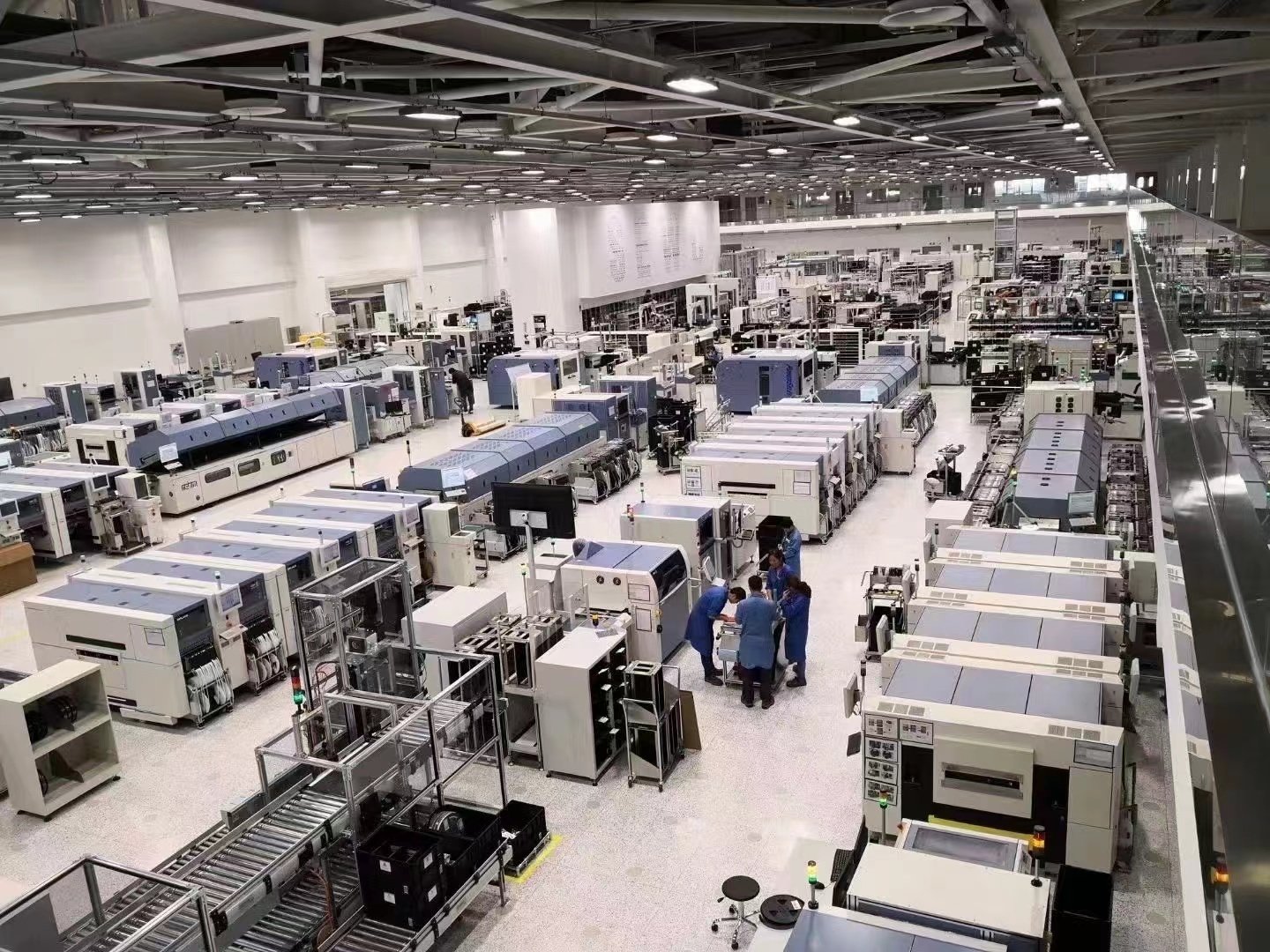


Our equipment
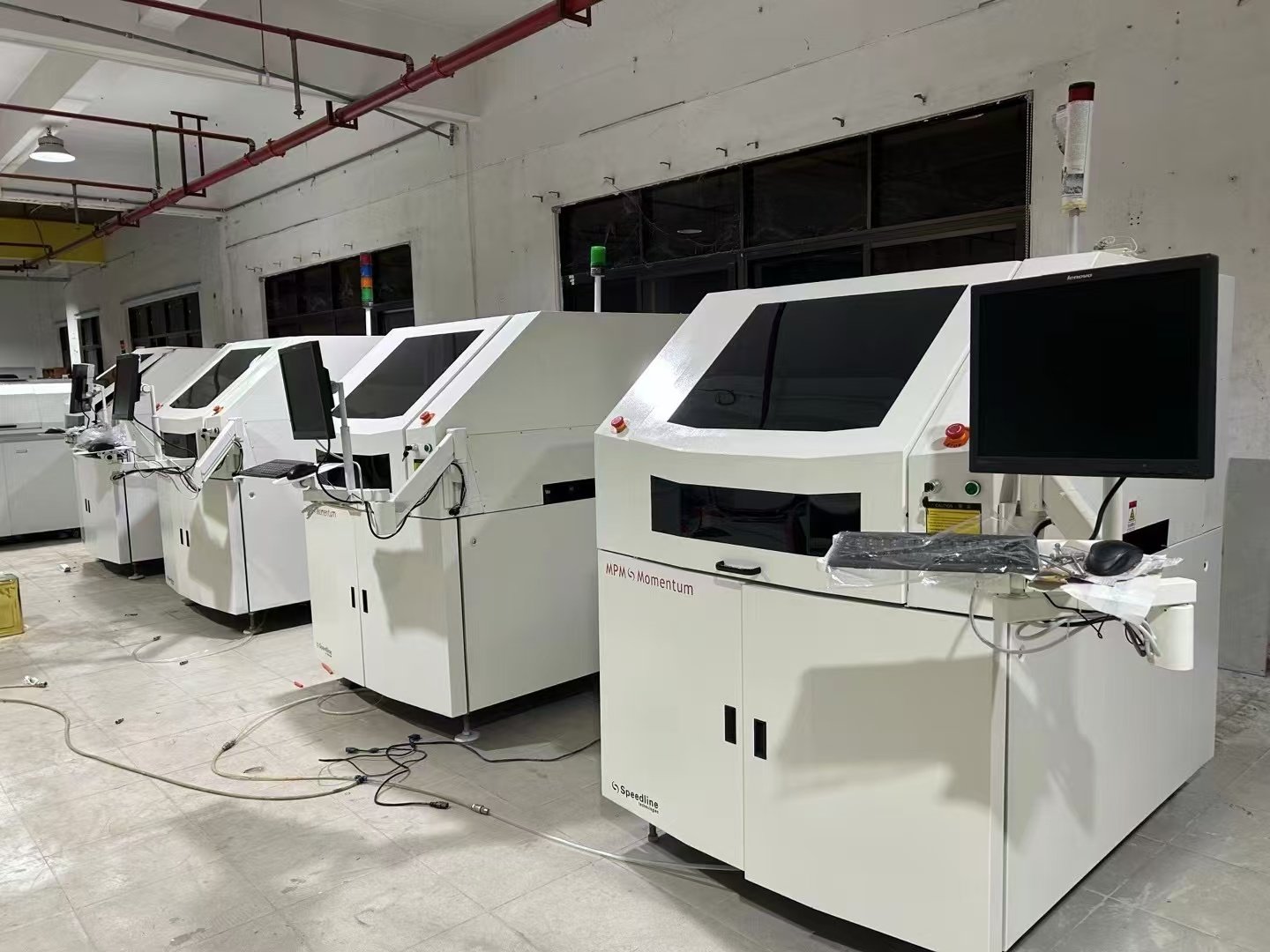
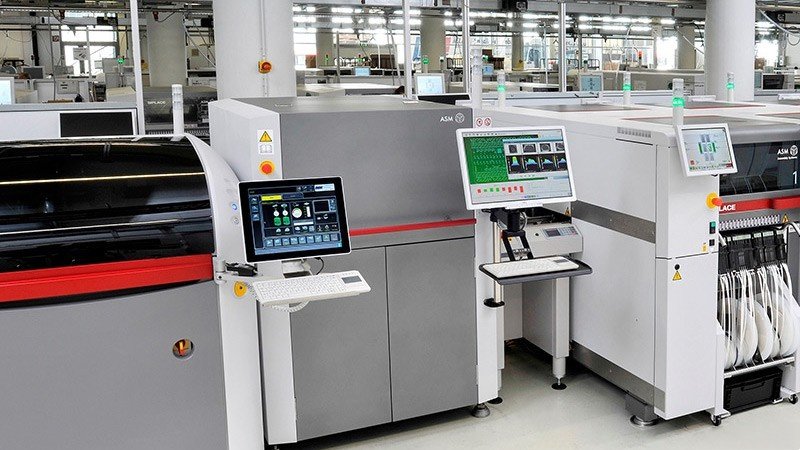




Surface Mount Technology in industrial manufacturing involves the automated assembly of electronic components directly onto PCBs, enabling efficient, high-volume production. SMT is integral to producing compact, high-performance devices, supporting industries like consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical technology by ensuring precision, reliability, and scalability in manufacturing.